Coordinated targeting of the EGFR signaling axis by microRNA-27a*
- PMID: 23963114
- PMCID: PMC3824521
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.1239
Coordinated targeting of the EGFR signaling axis by microRNA-27a*
Abstract
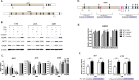
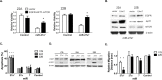
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) has been characterized as a critical factor in the development and progression of multiple solid tumors, including head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). However, monotherapy with EGFR-specific agents has not been as dramatic as preclinical studies have suggested. Since complex regulation of the EGFR signaling axis might confound current attempts to inhibit EGFR directly, we searched for microRNAs (miRNAs) that may target the EGFR signaling axis. We identified miR-27a (miR-27a-3p) and its complementary or star (*) strand, miR-27a* (miR-27a-5p), as novel miRNAs targeting EGFR, which were significantly downregulated in multiple HNSCC cell lines. Analysis of human specimens demonstrated that miR-27a* is significantly underexpressed in HNSCC as compared to normal mucosa. Increased expression of miR-27a* in HNSCC produced a profound cytotoxic effect not seen with miR-27a. Analysis for potential targets of miR-27a* led to the identification of AKT1 (protein kinase B) and mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) within the EGFR signaling axis. Treatment with miR-27a* led to coordinated downregulation of EGFR, AKT1 and mTOR. Overexpression of EGFR signaling pathway components decreased the overall effect of miR-27a* on HNSCC cell viability. Constitutive and inducible expression of miR-27a* in a murine orthotopic xenograft model of oral cavity cancer led to decreased tumor growth. Direct intratumoral injection of miR-27a* inhibited tumor growth in vivo. These findings identify miR-27a* as a functional star sequence that exhibits novel coordinated regulation of the EGFR pathway in solid tumors and potentially represents a novel therapeutic option.
Figures
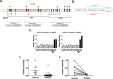
 ), −27a*(
), −27a*( ), −27b(
), −27b( ), −27b*(#), −7(
), −27b*(#), −7( ), −128(
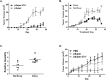
), −128( ) candidate binding sites within EGFR mRNA using in silico screening methods; (B) Hairpin representation of the pre-miR-27a with the sequences of miR-27a* (green) and miR-27a (magenta) highlighted; (C) Decreased expression of mature miR-27a and −27a* by qRT-PCR in 10 HNSCC cell lines and normal oral keratinocytes (OKF-6 and HOK16B). Values normalized to OKF-6, p<0.005; (D) Analysis of miR-27a* RNA in human HNSCC and normal mucosal specimens by qRT-PCR revealed an overall decrease in miR-27a* expression levels in HNSCC, p<0.0001; (E) Comparison of miR-27a* levels in matched normal/HNSCC tissue pairs demonstrated decreased expression in the tumors as compared to matched normal tissue, p<0.01.
) candidate binding sites within EGFR mRNA using in silico screening methods; (B) Hairpin representation of the pre-miR-27a with the sequences of miR-27a* (green) and miR-27a (magenta) highlighted; (C) Decreased expression of mature miR-27a and −27a* by qRT-PCR in 10 HNSCC cell lines and normal oral keratinocytes (OKF-6 and HOK16B). Values normalized to OKF-6, p<0.005; (D) Analysis of miR-27a* RNA in human HNSCC and normal mucosal specimens by qRT-PCR revealed an overall decrease in miR-27a* expression levels in HNSCC, p<0.0001; (E) Comparison of miR-27a* levels in matched normal/HNSCC tissue pairs demonstrated decreased expression in the tumors as compared to matched normal tissue, p<0.01.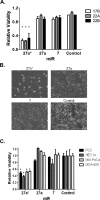
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-186 serves as a tumor suppressor in oral squamous cell carcinoma by negatively regulating the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP2 expression.Arch Oral Biol. 2018 May;89:20-25. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2018.01.016. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Arch Oral Biol. 2018. PMID: 29407635
-
Dual-receptor (EGFR and c-MET) inhibition by tumor-suppressive miR-1 and miR-206 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.J Hum Genet. 2017 Jan;62(1):113-121. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2016.47. Epub 2016 May 12. J Hum Genet. 2017. PMID: 27169691
-
MiR-206 inhibits Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell progression by targeting HDAC6 via PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Dec;96:229-237. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.08.145. Epub 2017 Oct 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28987947
-
EGFR-PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas: attractive targets for molecular-oriented therapy.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2011 Jan;15(1):63-74. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2011.541440. Epub 2010 Nov 26. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2011. PMID: 21110697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting EGFR-PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling enhances radiosensitivity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2015 Jun;19(6):795-805. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2015.1012157. Epub 2015 Feb 5. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2015. PMID: 25652792 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of MicroRNAs in Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System-Mediated Cardiovascular Inflammation and Remodeling.Int J Inflam. 2015;2015:101527. doi: 10.1155/2015/101527. Epub 2015 May 6. Int J Inflam. 2015. PMID: 26064773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-873 mediates multidrug resistance in ovarian cancer cells by targeting ABCB1.Tumour Biol. 2016 Aug;37(8):10499-506. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-4944-y. Epub 2016 Feb 5. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26850595
-
Targeting AKT/mTOR in Oral Cancer: Mechanisms and Advances in Clinical Trials.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 6;21(9):3285. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093285. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32384682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-27a-5p regulation by promoter methylation and MYC signaling in prostate carcinogenesis.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Feb 7;9(2):167. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0241-y. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29415999 Free PMC article.
-
The Poly-cistronic miR-23-27-24 Complexes Target Endothelial Cell Junctions: Differential Functional and Molecular Effects of miR-23a and miR-23b.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2016 Aug 23;5(8):e354. doi: 10.1038/mtna.2016.62. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2016. PMID: 27741223 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J CLin. 2010;60(5):277–300. - PubMed
-
- Rubin Grandis J, Melhem MF, Gooding WE, Day R, Holst VA, Wagener MM, Drenning SD, Tweardy DJ. Levels of TGF-alpha and EGFR protein in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and patient survival. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998;90(11):824–832. - PubMed
-
- Ang KK, Berkey BA, Tu X, Zhang HZ, Katz R, Hammond EH, Fu KK, Milas L. Impact of epidermal growth factor receptor expression on survival and pattern of relapse in patients with advanced head and neck carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2002;62(24):7350–7356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

