Superantigens are critical for Staphylococcus aureus Infective endocarditis, sepsis, and acute kidney injury
- PMID: 23963178
- PMCID: PMC3747586
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00494-13
Superantigens are critical for Staphylococcus aureus Infective endocarditis, sepsis, and acute kidney injury
Abstract
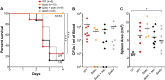
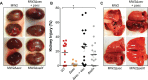
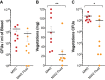
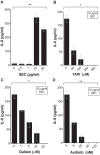
Infective endocarditis and kidney infections are serious complications of Staphylococcus aureus sepsis. We investigated the role of superantigens (SAgs) in the development of lethal sepsis, infective endocarditis, and kidney infections. SAgs cause toxic shock syndrome, but it is unclear if SAgs contribute to infective endocarditis and kidney infections secondary to sepsis. We show in the methicillin-resistant S. aureus strain MW2 that lethal sepsis, infective endocarditis, and kidney infections in rabbits are critically dependent on high-level SAgs. In contrast, the isogenic strain lacking staphylococcal enterotoxin C (SEC), the major SAg in this strain, is attenuated in virulence, while complementation restores disease production. SAgs' role in infective endocarditis appears to be both superantigenicity and direct endothelial cell stimulation. Maintenance of elevated blood pressure by fluid therapy significantly protects from infective endocarditis, possibly through preventing bacterial accumulation on valves and increased SAg elimination. These data should facilitate better methods to manage these serious illnesses.
Importance: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported in 2007 that Staphylococcus aureus is the most significant cause of serious infectious diseases in the United States (R. M. Klevens, M. A. Morrison, J. Nadle, S. Petit, K. Gershman, et al., JAMA 298:1763-1771, 2007). Among these infections are sepsis, infective endocarditis, and acute kidney injury. Infective endocarditis occurs in 30 to 60% of patients with S. aureus bacteremia and carries a mortality rate of 40 to 50%. Over the past decades, infective endocarditis outcomes have not improved, and infection rates are steadily increasing (D. H. Bor, S. Woolhandler, R. Nardin, J. Brusch, D. U. Himmelstein, PLoS One 8:e60033, 2013). There is little understanding of the S. aureus virulence factors that are key for infective endocarditis development and kidney abscess formation. We demonstrate that superantigens are critical in the causation of all three infections. We show that their association results from both superantigenicity and direct toxic effects on endothelial cells, the latter likely contributing to delayed endothelium healing. Our studies contribute significantly to understanding the development of these illnesses and are expected to lead to development of important therapies to treat such illnesses.
Figures


References
-
- Murdoch DR, Corey GR, Hoen B, Miró JM, Fowler VG, Bayer AS, Karchmer AW, Olaison L, Pappas PA, Moreillon P, Chambers ST, Chu VH, Falcó V, Holland DJ, Jones P, Klein JL, Raymond NJ, Read KM, Tripodi MF, Utili R, Wang A, Woods CW, Cabell CH, International Collaboration on Endocarditis-Prospective Cohort Study (ICE-PCS) Investigators 2009. Clinical presentation, etiology, and outcome of infective endocarditis in the 21st century: the International Collaboration on Endocarditis-Prospective Cohort Study. Arch. Intern. Med. 169:463–473 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shorr AF, Tabak YP, Killian AD, Gupta V, Liu LZ, Kollef MH. 2006. Health care-associated bloodstream infection: A distinct entity? Insights from large U.S. database. Crit. Care Med 34:2588–2595 - PubMed
-
- Fowler VG, Jr, Miro JM, Hoen B, Cabell CH, Abrutyn E, Rubinstein E, Corey GR, Spelman D, Bradley SF, Barsic B, Pappas PA, Anstrom KJ, Wray D, Fortes CQ, Anguera I, Athan E, Jones P, van der Meer JT, Elliott TS, Levine DP, Bayer AS, ICE Investigators 2005. Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis: a consequence of medical progress. JAMA 293:3012–3021 - PubMed
-
- Naber CK. 2009. Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management strategies. Clin. Infect. Dis. 48(Suppl 4):S231–S237 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
