Silibinin suppresses EMT-driven erlotinib resistance by reversing the high miR-21/low miR-200c signature in vivo
- PMID: 23963283
- PMCID: PMC3748425
- DOI: 10.1038/srep02459
Silibinin suppresses EMT-driven erlotinib resistance by reversing the high miR-21/low miR-200c signature in vivo
Abstract
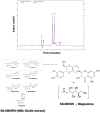
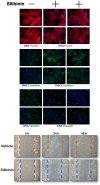
The flavolignan silibinin was studied for its ability to restore drug sensitivity to EGFR-mutant NSCLC xenografts with epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-driven resistance to erlotinib. As a single agent, silibinin significantly decreased the tumor volumes of erlotinib-refractory NSCLC xenografts by approximately 50%. Furthermore, the complete abrogation of tumor growth was observed with the co-treatment of erlotinib and silibinin. Silibinin fully reversed the EMT-related high miR-21/low miR-200c microRNA signature and repressed the mesenchymal markers SNAIL, ZEB, and N-cadherin observed in erlotinib-refractory tumors. Silibinin was sufficient to fully activate a reciprocal mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition (MET) in erlotinib-refractory cells and prevent the highly migratogenic phenotype of erlotinib-resistant NSCLC cells. Given that the various mechanisms of resistance to erlotinib result from EMT, regardless of the EGFR mutation status, a water-soluble, silibinin-rich milk thistle extract might be a suitable candidate therapy for upcoming clinical trials aimed at preventing or reversing NSCLC progression following erlotinib treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
AstraZeneca (Spain) provided partial financial support for the present study via an educational grant to Dr. Javier A. Menendez and Dr. Joaquim Bosch-Barrera.
Figures




References
-
- Rosell R. et al. Screening for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 361, 958–67 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Rosell R. et al. Predictive biomarkers in the management of EGFR mutant lung cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1210, 45–52 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Rosell R. et al. Non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations in the EGFR kinase domain. Clin Transl Oncol 12, 75–80 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Rosell R. et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 13, 239–46 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Santarpia M., De Pas T. M., Altavilla G., Spaggiari L. & Rosell R. Moving towards molecular-guided treatments: erlotinib and clinical outcomes in non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Future Oncol 9, 327–45 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

