Homotypic versican G1 domain interactions enhance hyaluronan incorporation into fibrillin microfibrils
- PMID: 23963449
- PMCID: PMC3790016
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.456947
Homotypic versican G1 domain interactions enhance hyaluronan incorporation into fibrillin microfibrils
Abstract
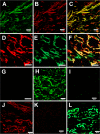
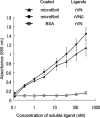
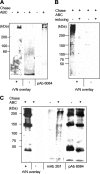
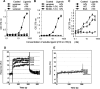
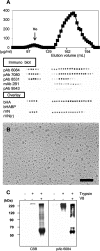
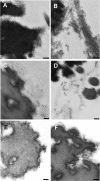
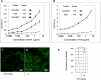
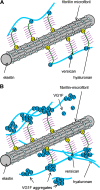
Versican G1 domain-containing fragments (VG1Fs) have been identified in extracts from the dermis in which hyaluronan (HA)-versican-fibrillin complexes are found. However, the molecular assembly of VG1Fs in the HA-versican-microfibril macrocomplex has not yet been elucidated. Here, we clarify the role of VG1Fs in the extracellular macrocomplex, specifically in mediating the recruitment of HA to microfibrils. Sequential extraction studies suggested that the VG1Fs were not associated with dermal elements through HA binding properties alone. Overlay analyses of dermal tissue sections using the recombinant versican G1 domain, rVN, showed that rVN deposited onto the elastic fiber network. In solid-phase binding assays, rVN bound to isolated nondegraded microfibrils. rVN specifically bound to authentic versican core protein produced by dermal fibroblasts. Furthermore, rVN bound to VG1Fs extracted from the dermis and to nondenatured versican but not to fibrillin-1. Homotypic binding of rVN was also seen. Consistent with these binding properties, macroaggregates containing VG1Fs were detected in high molecular weight fractions of sieved dermal extracts and visualized by electron microscopy, which revealed localization to microfibrils at the microscopic level. Importantly, exogenous rVN enhanced HA recruitment both to isolated microfibrils and to microfibrils in tissue sections in a dose-dependent manner. From these data, we propose that cleaved VG1Fs can be recaptured by microfibrils through VG1F homotypical interactions to enhance HA recruitment to microfibrils.
Keywords: ADAM ADAMTS; Dermis; Extracellular Matrix; Fibrillin; Hyaluronate; Proteoglycan; Versican.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Versican, a major hyaluronan-binding component in the dermis, loses its hyaluronan-binding ability in solar elastosis.J Invest Dermatol. 2007 Jul;127(7):1657-63. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700754. Epub 2007 Mar 15. J Invest Dermatol. 2007. PMID: 17363913
-
The Versican G1 Fragment and Serum-Derived Hyaluronan-Associated Proteins Interact and Form a Complex in Granulation Tissue of Pressure Ulcers.Am J Pathol. 2018 Feb;188(2):432-449. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2017.10.015. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Am J Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29169988
-
Versican and fibrillin-1 form a major hyaluronan-binding complex in the ciliary body.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008 Jul;49(7):2870-7. doi: 10.1167/iovs.07-1488. Epub 2008 Apr 4. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008. PMID: 18390636
-
Fibrillin-rich microfibrils: elastic biopolymers of the extracellular matrix.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2002;23(5-6):581-96. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2002. PMID: 12785107 Review.
-
Fibrillin: from microfibril assembly to biomechanical function.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2002 Feb 28;357(1418):207-17. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2001.1029. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2002. PMID: 11911778 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of the Extracellular Matrix in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Pulmonary Emphysema.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 2;25(19):10613. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910613. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Versican and the regulation of cell phenotype in disease.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Aug;1840(8):2441-51. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.12.028. Epub 2014 Jan 5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24401530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G1 Domain of Versican Regulates Hyaluronan Organization and the Phenotype of Cultured Human Dermal Fibroblasts.J Histochem Cytochem. 2016 Jun;64(6):353-63. doi: 10.1369/0022155416643913. Epub 2016 Apr 28. J Histochem Cytochem. 2016. PMID: 27126822 Free PMC article.
-
Desmosine: The Rationale for Its Use as a Biomarker of Therapeutic Efficacy in the Treatment of Pulmonary Emphysema.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Feb 27;15(5):578. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15050578. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40075825 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the versican interactome in lung health and disease.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022 Aug 1;323(2):C249-C276. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00162.2022. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35649251 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Feinberg T., Weiss S. J. (2009) Developmental ECM sculpting. Laying it down and cutting it up. Dev. Cell. 17, 584–586 - PubMed
-
- Kimata K., Oike Y., Tani K., Shinomura T., Yamagata M., Uritani M., Suzuki S. (1986) A large chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan (PG-M) synthesized before chondrogenesis in the limb bud of chick-embryo. J. Biol. Chem. 261, 13517–13525 - PubMed
-
- LeBaron R. G., Zimmermann D. R., Ruoslahti E. (1992) Hyaluronate binding-properties of versican. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 10003–10010 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

