Role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in lung inflammation
- PMID: 23963493
- PMCID: PMC3821999
- DOI: 10.1007/s00281-013-0391-7
Role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in lung inflammation
Abstract
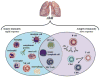
Millions of individuals worldwide are afflicted with acute and chronic respiratory diseases, causing temporary and permanent disabilities and even death. Oftentimes, these diseases occur as a result of altered immune responses. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), a ligand-activated transcription factor, acts as a regulator of mucosal barrier function and may influence immune responsiveness in the lungs through changes in gene expression, cell-cell adhesion, mucin production, and cytokine expression. This review updates the basic immunobiology of the AhR signaling pathway with regards to inflammatory lung diseases such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and silicosis following data in rodent models and humans. Finally, we address the therapeutic potential of targeting the AhR in regulating inflammation during acute and chronic respiratory diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kewley RJ, Whitelaw ML, Chapman-Smith A. The mammalian basic helix-loop-helix/PAS family of transcriptional regulators. The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology. 2004;36:189–204. - PubMed
-
- Frericks M, Meissner M, Esser C. Microarray analysis of the AHR system: tissue-specific flexibility in signal and target genes. Toxicology and applied pharmacology. 2007;220:320–32. - PubMed
-
- Ema M, Matsushita N, Sogawa K, Ariyama T, Inazawa J, Nemoto T, Ota M, Oshimura M, Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Human arylhydrocarbon receptor: functional expression and chromosomal assignment to 7p21. Journal of biochemistry. 1994;116:845–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical