The Arabidopsis metacaspase9 degradome
- PMID: 23964026
- PMCID: PMC3784583
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.113.115287
The Arabidopsis metacaspase9 degradome
Abstract
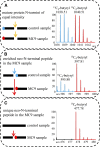
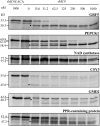
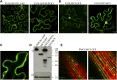
Metacaspases are distant relatives of the metazoan caspases, found in plants, fungi, and protists. However, in contrast with caspases, information about the physiological substrates of metacaspases is still scarce. By means of N-terminal combined fractional diagonal chromatography, the physiological substrates of metacaspase9 (MC9; AT5G04200) were identified in young seedlings of Arabidopsis thaliana on the proteome-wide level, providing additional insight into MC9 cleavage specificity and revealing a previously unknown preference for acidic residues at the substrate prime site position P1'. The functionalities of the identified MC9 substrates hinted at metacaspase functions other than those related to cell death. These results allowed us to resolve the substrate specificity of MC9 in more detail and indicated that the activity of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1 (AT4G37870), a key enzyme in gluconeogenesis, is enhanced upon MC9-dependent proteolysis.
Figures




References
-
- Abramoff M., Magalhães P., Ram S. (2004). Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics International 11: 36–42
-
- Ambit A., Fasel N., Coombs G.H., Mottram J.C. (2008). An essential role for the Leishmania major metacaspase in cell cycle progression. Cell Death Differ. 15: 113–122 - PubMed
-
- Aravind L., Dixit V.M., Koonin E.V. (1999). The domains of death: Evolution of the apoptosis machinery. Trends Biochem. Sci. 24: 47–53 - PubMed
-
- Aravind L., Koonin E.V. (2002). Classification of the caspase-hemoglobinase fold: Detection of new families and implications for the origin of the eukaryotic separins. Proteins 46: 355–367 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

