Portal hypertension and gastrointestinal bleeding: diagnosis, prevention and management
- PMID: 23964137
- PMCID: PMC3746375
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i31.5035
Portal hypertension and gastrointestinal bleeding: diagnosis, prevention and management
Abstract
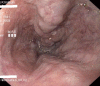
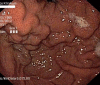
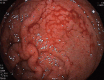
Bleeding from esophageal varices is a life threatening complication of portal hypertension. Primary prevention of bleeding in patients at risk for a first bleeding episode is therefore a major goal. Medical prophylaxis consists of non-selective beta-blockers like propranolol or carvedilol. Variceal endoscopic band ligation is equally effective but procedure related morbidity is a drawback of the method. Therapy of acute bleeding is based on three strategies: vasopressor drugs like terlipressin, antibiotics and endoscopic therapy. In refractory bleeding, self-expandable stents offer an option for bridging to definite treatments like transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS). Treatment of bleeding from gastric varices depends on vasopressor drugs and on injection of varices with cyanoacrylate. Strategies for primary or secondary prevention are based on non-selective beta-blockers but data from large clinical trials is lacking. Therapy of refractory bleeding relies on shunt-procedures like TIPS. Bleeding from ectopic varices, portal hypertensive gastropathy and gastric antral vascular ectasia-syndrome is less common. Possible medical and endoscopic treatment options are discussed.
Keywords: Band ligation; Beta-blocker; Endoscopy; Esophageal varices; Gastric antral vascular ectasia-syndrome; Gastric varices; Portal hypertension; Portal hypertensive gastropathy; Variceal bleeding.
Figures



References
-
- Calès P, Pascal JP. Natural history of esophageal varices in cirrhosis (from origin to rupture) Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1988;12:245–254. - PubMed
-
- D’Amico G, Pagliaro L, Bosch J. The treatment of portal hypertension: a meta-analytic review. Hepatology. 1995;22:332–354. - PubMed
-
- Abraldes JG, Villanueva C, Bañares R, Aracil C, Catalina MV, Garci A-Pagán JC, Bosch J. Hepatic venous pressure gradient and prognosis in patients with acute variceal bleeding treated with pharmacologic and endoscopic therapy. J Hepatol. 2008;48:229–236. - PubMed
-
- Augustin S, Altamirano J, González A, Dot J, Abu-Suboh M, Armengol JR, Azpiroz F, Esteban R, Guardia J, Genescà J. Effectiveness of combined pharmacologic and ligation therapy in high-risk patients with acute esophageal variceal bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106:1787–1795. - PubMed
-
- Villanueva C, Piqueras M, Aracil C, Gómez C, López-Balaguer JM, Gonzalez B, Gallego A, Torras X, Soriano G, Sáinz S, et al. A randomized controlled trial comparing ligation and sclerotherapy as emergency endoscopic treatment added to somatostatin in acute variceal bleeding. J Hepatol. 2006;45:560–567. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

