Bamboo salt attenuates CCl4-induced hepatic damage in Sprague-Dawley rats
- PMID: 23964314
- PMCID: PMC3746161
- DOI: 10.4162/nrp.2013.7.4.273
Bamboo salt attenuates CCl4-induced hepatic damage in Sprague-Dawley rats
Abstract
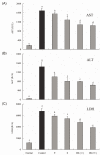
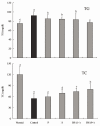
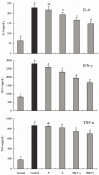
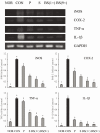
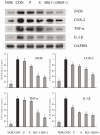
Bamboo salt, a Korean folk medicine, is prepared with solar salt (sea salt) and baked several times at high temperatures in a bamboo case. In this study, we compared the preventive effects of bamboo salt and purified and solar salts on hepatic damage induced by carbon tetrachloride in Sprague-Dawley rats. Compared with purified and solar salts, bamboo salts prevented hepatic damage in rats, as evidenced by significantly reduced serum levels of aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, and lactate dehydrogenase (P < 0.05). Bamboo salt (baked 9×) triggered the greatest reduction in these enzyme levels. In addition, it also reduced the levels of the proinflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-6, interferon (IFN)-γ, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α. Histopathological sections of liver tissue demonstrated the protective effect of bamboo salt, whereas sections from animals treated with the other salt groups showed a greater degree of necrosis. We also performed reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and western blot analyses of the inflammation-related genes iNOS, COX-2, TNF-α, and IL-1β in rat liver tissues. Bamboo salt induced a significant decrease (~80%) in mRNA and protein expression levels of COX-2, iNOS, TNF-α, and IL-1β, compared with the other salts. Thus, we found that baked bamboo salt preparations could prevent CCl4-induced hepatic damage in vivo.
Keywords: Bamboo salt; CCl4; cytokines; hepatic damage; inflammation.
Figures

References
-
- Hu C, Zhang Y, Kitts DD. Evaluation of antioxidant and prooxidant activities of bamboo Phyllostachys nigra var. Henonis leaf extract in vitro. J Agric Food Chem. 2000;48:3170–3176. - PubMed
-
- Shin HY, Na HJ, Moon PD, Seo SW, Shin TY, Hong SH, Lee KN, Park RK, Kim HM. Biological activity of bamboo salt. Food Ind Nutr. 2004;9:36–45.
-
- Shin HY, Lee EH, Kim CY, Shin TY, Kim SD, Song YS, Lee KN, Hong SH, Kim HM. Anti-inflammatory activity of Korean folk medicine purple bamboo salt. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2003;25:377–384. - PubMed
-
- Cauwels A, Brouckaert P. Survival of TNF toxicity: dependence on caspases and NO. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2007;462:132–139. - PubMed
-
- Seitz HK, Stickel F. Risk factors and mechanisms of hepatocarcinogenesis with special emphasis on alcohol and oxidative stress. Biol Chem. 2006;387:349–360. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

