HIV immune activation drives increased Eomes expression in memory CD8 T cells in association with transcriptional downregulation of CD127
- PMID: 23965471
- PMCID: PMC7577351
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e3283618487
HIV immune activation drives increased Eomes expression in memory CD8 T cells in association with transcriptional downregulation of CD127
Abstract
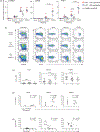
Background: During HIV infection distinct mechanisms drive immune activation of the CD4 and CD8 T cells leading to CD4 T-cell depletion and expansion of the CD8 T-cell pool. This immune activation is polyclonal and extends beyond HIV-specific T cells. One consequence of this immune activation is a profound decrease in IL-7Rα (CD127) expression on memory CD8 T cells. The mechanisms leading to this are unknown and because of the potential impact of reduced IL-7 signaling in memory T cells specific to HIV and other pathogens, in the present study we examined the molecular mechanisms implicated in this downregulation of CD127.
Methods: Membrane bound (mIL7RA) and soluble (sIL7RA) mRNA expression was determined by qRT-PCR. CD127, Eomesodermin (Eomes) and T-bet expression in healthy controls and HIV-infected patients were studied by flow cytometry.
Results: CD127 downregulation occurs at the transcriptional level for both mIL7RA and sIL7RA alternative spliced forms in the CD127 memory CD8 T cells. CD127 memory CD8 T cells exhibited increased Eomes expression and an 'effector-like' gene profile. These changes were associated with higher HIV-RNA levels. Following combination antiretroviral therapy (cART), there was an increase in CD127 expression over an extended period of time (>5 months) which was associated with decreased Eomes expression.
Conclusion: CD127 is downregulated at a transcriptional level in memory CD8 T cells in association with upregulation of Eomes expression.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Doisne JM, Urrutia A, Lacabaratz-Porret C, Goujard C, Meyer L, Chaix ML, et al. CD8+ T cells specific for EBV, cytomegalovirus, and influenza virus are activated during primary HIV infection. J Immunol 2004; 173:2410–2418. - PubMed
-
- Giorgi JV, Hultin LE, McKeating JA, Johnson TD, Owens B, Jacobson LP, et al. Shorter survival in advanced human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection is more closely associated with T lymphocyte activation than with plasma virus burden or virus chemokine coreceptor usage. J Infect Dis 1999; 179:859–870. - PubMed
-
- Ho HN, Hultin LE, Mitsuyasu RT, Matud JL, Hausner MA, Bockstoce D, et al. Circulating HIV-specific CD8+ cytotoxic T cells express CD38 and HLA-DR antigens. J Immunol 1993; 150:3070–3079. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

