Modeling the interaction of dodecylphosphocholine micelles with the anticoccidial peptide PW2 guided by NMR data
- PMID: 23966088
- PMCID: PMC6270265
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules180810056
Modeling the interaction of dodecylphosphocholine micelles with the anticoccidial peptide PW2 guided by NMR data
Abstract
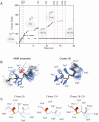
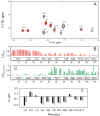
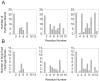
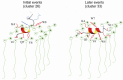
Antimicrobial peptides are highly dynamic entities that acquire structure upon binding to a membrane interface. To better understand the structure and the mechanism for the molecular recognition of dodecylphosphocholine (DPC) micelles by the anticoccidial peptide PW2, we performed molecular dynamics (MD) simulations guided by NMR experimental data, focusing on strategies to explore the transient nature of micelles, which rearrange on a millisecond to second timescale. We simulated the association of PW2 with a pre-built DPC micelle and with free-DPC molecules that spontaneously forms micelles in the presence of the peptide along the simulation. The simulation with spontaneous micelle formation provided the adequate environment which replicated the experimental data. The unrestrained MD simulations reproduced the NMR structure for the entire 100 ns MD simulation time. Hidden discrete conformational states could be described. Coulomb interactions are important for initial approximation and hydrogen bonds for anchoring the aromatic region at the interface, being essential for the stabilization of the interaction. Arg9 is strongly attached with phosphate. We observed a helix elongation process stabilized by the intermolecular peptide-micelle association. Full association that mimics the experimental data only happens after complete micelle re-association. Fast micelle dynamics without dissociation of surfactants leads to only superficial binding.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effect of micelle interface on the binding of anticoccidial PW2 peptide.J Biomol NMR. 2007 Dec;39(4):315-22. doi: 10.1007/s10858-007-9202-6. Epub 2007 Oct 10. J Biomol NMR. 2007. PMID: 17926009
-
Bindings of hMRP1 transmembrane peptides with dodecylphosphocholine and dodecyl-β-d-maltoside micelles: a molecular dynamics simulation study.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1838(1 Pt B):493-509. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.10.012. Epub 2013 Oct 21. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24157718
-
Molecular dynamics simulation of adrenocorticotropin (1-10) peptide in a solvated dodecylphosphocholine micelle.Biopolymers. 2001 Jun;58(7):643-59. doi: 10.1002/1097-0282(200106)58:7<643::AID-BIP1037>3.0.CO;2-R. Biopolymers. 2001. PMID: 11285560
-
Molecular dynamics simulations of adrenocorticotropin (1-24) peptide in a solvated dodecylphosphocholine (DPC) micelle and in a dimyistoylphosphatidylcholine (DMPC) bilayer.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2002 Aug;20(1):39-57. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2002.10506821. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2002. PMID: 12144351
-
Solution NMR of membrane proteins in bilayer mimics: small is beautiful, but sometimes bigger is better.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Dec;1768(12):3098-106. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.09.006. Epub 2007 Sep 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17961504 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural and Dynamic Insights of the Interaction between Tritrpticin and Micelles: An NMR Study.Biophys J. 2016 Dec 20;111(12):2676-2688. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.10.034. Biophys J. 2016. PMID: 28002744 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering Structure-Function Relationship Unveils Salt-Resistant Mode of Action of a Potent MRSA-Inhibiting Antimicrobial Peptide, RR14.J Bacteriol. 2022 Dec 20;204(12):e0031222. doi: 10.1128/jb.00312-22. Epub 2022 Nov 15. J Bacteriol. 2022. PMID: 36377870 Free PMC article.
-
A Dynamic Overview of Antimicrobial Peptides and Their Complexes.Molecules. 2018 Aug 15;23(8):2040. doi: 10.3390/molecules23082040. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30111717 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Thomma B.P.H.J., Cammue B.P.A., Thevissen K. Mode of action of plant defensins suggests therapeutic potential. Curr. Drug Targets Infect. Disord. 2003;3:1–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

