Auditory sensitivity of larval zebrafish (Danio rerio) measured using a behavioral prepulse inhibition assay
- PMID: 23966590
- PMCID: PMC3749908
- DOI: 10.1242/jeb.087635
Auditory sensitivity of larval zebrafish (Danio rerio) measured using a behavioral prepulse inhibition assay
Abstract
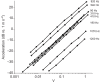
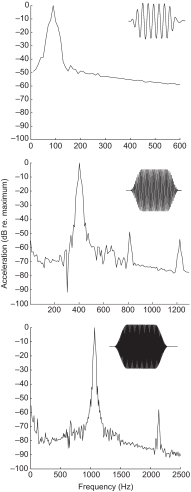
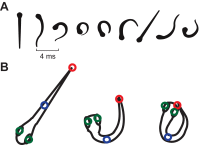
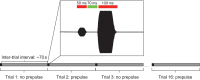
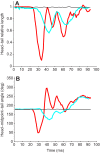
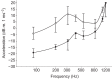
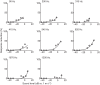
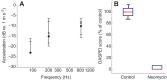
Zebrafish (Danio rerio) have become a valuable model for investigating the molecular genetics and development of the inner ear in vertebrates. In this study, we employed a prepulse inhibition (PPI) paradigm to assess hearing in larval wild-type (AB) zebrafish during early development at 5-6 days post-fertilization (d.p.f.). We measured the PPI of the acoustic startle response in zebrafish using a 1-dimensional shaker that simulated the particle motion component of sound along the fish's dorsoventral axis. The thresholds to startle-inducing stimuli were determined in 5-6 d.p.f. zebrafish, and their hearing sensitivity was then characterized using the thresholds of prepulse tone stimuli (90-1200 Hz) that inhibited the acoustic startle response to a reliable startle stimulus (820 Hz at 20 dB re. 1 m s(-2)). Hearing thresholds were defined as the minimum prepulse tone level required to significantly reduce the startle response probability compared with the baseline (no-prepulse) condition. Larval zebrafish showed greatest auditory sensitivity from 90 to 310 Hz with corresponding mean thresholds of -19 to -10 dB re. 1 m s(-2), respectively. Hearing thresholds of prepulse tones were considerably lower than previously predicted by startle response assays. The PPI assay was also used to investigate the relative contribution of the lateral line to the detection of acoustic stimuli. After aminoglycoside-induced neuromast hair-cell ablation, we found no difference in PPI thresholds between treated and control fish. We propose that this PPI assay can be used to screen for novel zebrafish hearing mutants and to investigate the ontogeny of hearing in zebrafish and other fishes.
Keywords: hearing; lateral line; sensorimotor; startle response.
Figures

References
-
- Bang P. I., Sewell W. F., Malicki J. J. (2000). Behavioral screen for dominant mutations affecting zebrafish auditory system. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. Abs. 23, 177-187
-
- Bang P. I., Sewell W. F., Malicki J. J. (2001). Morphology and cell type heterogeneities of the inner ear epithelia in adult and juvenile zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Comp. Neurol. 438, 173-190 - PubMed
-
- Bang P. I., Yelick P. C., Malicki J. J., Sewell W. F. (2002). High-throughput behavioral screening method for detecting auditory response defects in zebrafish. J. Neurosci. Methods 118, 177-187 - PubMed
-
- Buck L. M. J., Winter M. J., Redfern W. S., Whitfield T. T. (2012). Ototoxin-induced cellular damage in neuromasts disrupts lateral line function in larval zebrafish. Hear. Res. 284, 67-81 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

