Genome-wide association of body fat distribution in African ancestry populations suggests new loci
- PMID: 23966867
- PMCID: PMC3744443
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003681
Genome-wide association of body fat distribution in African ancestry populations suggests new loci
Abstract
Central obesity, measured by waist circumference (WC) or waist-hip ratio (WHR), is a marker of body fat distribution. Although obesity disproportionately affects minority populations, few studies have conducted genome-wide association study (GWAS) of fat distribution among those of predominantly African ancestry (AA). We performed GWAS of WC and WHR, adjusted and unadjusted for BMI, in up to 33,591 and 27,350 AA individuals, respectively. We identified loci associated with fat distribution in AA individuals using meta-analyses of GWA results for WC and WHR (stage 1). Overall, 25 SNPs with single genomic control (GC)-corrected p-values<5.0 × 10(-6) were followed-up (stage 2) in AA with WC and with WHR. Additionally, we interrogated genomic regions of previously identified European ancestry (EA) WHR loci among AA. In joint analysis of association results including both Stage 1 and 2 cohorts, 2 SNPs demonstrated association, rs2075064 at LHX2, p = 2.24×10(-8) for WC-adjusted-for-BMI, and rs6931262 at RREB1, p = 2.48×10(-8) for WHR-adjusted-for-BMI. However, neither signal was genome-wide significant after double GC-correction (LHX2: p = 6.5 × 10(-8); RREB1: p = 5.7 × 10(-8)). Six of fourteen previously reported loci for waist in EA populations were significant (p<0.05 divided by the number of independent SNPs within the region) in AA studied here (TBX15-WARS2, GRB14, ADAMTS9, LY86, RSPO3, ITPR2-SSPN). Further, we observed associations with metabolic traits: rs13389219 at GRB14 associated with HDL-cholesterol, triglycerides, and fasting insulin, and rs13060013 at ADAMTS9 with HDL-cholesterol and fasting insulin. Finally, we observed nominal evidence for sexual dimorphism, with stronger results in AA women at the GRB14 locus (p for interaction = 0.02). In conclusion, we identified two suggestive loci associated with fat distribution in AA populations in addition to confirming 6 loci previously identified in populations of EA. These findings reinforce the concept that there are fat distribution loci that are independent of generalized adiposity.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00005267.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
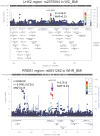
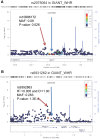

References
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Curtin LR (2010) Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2008. JAMA 303: 235–241. - PubMed
-
- Poirier P, Despres JP (2003) Waist circumference, visceral obesity, and cardiovascular risk. J Cardiopulm Rehabil 23: 161–169. - PubMed
-
- Pischon T, Boeing H, Hoffmann K, Bergmann M, Schulze MB, et al. (2008) General and abdominal adiposity and risk of death in Europe. N Engl J Med 359: 2105–2120. - PubMed
-
- Canoy D (2008) Distribution of body fat and risk of coronary heart disease in men and women. Curr Opin Cardiol 23: 591–598. - PubMed
-
- Ohlson LO, Larsson B, Svardsudd K, Welin L, Eriksson H, et al. (1985) The influence of body fat distribution on the incidence of diabetes mellitus. 13.5 years of follow-up of the participants in the study of men born in 1913. Diabetes 34: 1055–1058. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U10 HL054472/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL054472/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA54281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-72992/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N02-HL-6-4278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071025/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-25195/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97068/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR033176/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-72997/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-088215/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97053/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC045204/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095095/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL054471/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL054496/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055016/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-73003/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085080/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 32105-6/PHS HHS/United States
- N01-HC-45205/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR033176/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095172/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES010126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 CA148085/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ES007784/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-05187/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-4804/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-071252/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL59684/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL053916/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055019/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL046380/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S06GM008016-380111/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071251/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC048048/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087698/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL054509/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-071258/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000150/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071259/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- MD002249/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HL071025-01A1/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA1326792/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015928/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA140388/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AG062101/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- S06GM008016-320107/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-7299/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL063463/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085082/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL085251/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK-8925601/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA098663/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071252/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97064/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL092577-01A1/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01HG200362/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR00080/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA63464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087660/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055021/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55022/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-H-97054/PHS HHS/United States
- N01AG62101/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-071250/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC015103/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55016/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085083/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL085251/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 32118/PHS HHS/United States
- U01 HL054509/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- NIH HL 46380/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-024156/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AG-15928/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 42107-26/PHS HHS/United States
- R56 AG020098/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 32115/PHS HHS/United States
- N01 WH022110/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-73002/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P20-RR-17696/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P60 MD002249/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97070/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC048049/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97056/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024156/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-72982/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085085/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-45204/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-72993/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071250/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 HG200362/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA100598/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-73000/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055015/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01AG032098-01A1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087652/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL076784/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG-20098/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95095/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL54515/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR000052/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HL087652/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97085/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AG062106/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HL58625-01A1/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL053938/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-071251/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55021/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK075681/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85086/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 32100-2/PHS HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA058223/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50-CA58223/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA068578/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HG004726/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-73005/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 32119/PHS HHS/United States
- U01 HL064360/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC045205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG-027058/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- CA63464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG032098/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 24152/PHS HHS/United States
- CA68578/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-48050/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055020/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-73006/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA058420/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200782096C/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-35129/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-45134/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC-55222/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 42129-32/PHS HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071051/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 MD006899/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077813/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-071259/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC025195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97071/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97066/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AG000513/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200036C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK084350/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA148085/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA164974/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55015/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL087660/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL54496/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 HL100245/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AG062103/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA058920/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095170/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL053941/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL55673/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA063464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000052/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-48049/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97051/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-72995/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS041588/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-071205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97062/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC045134/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-73001/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97060/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 32108-9/PHS HHS/United States
- N01 HC005187/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-75150/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- NR0224103/NR/NINR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55020/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-087700/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL72518/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC-15103/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK-075681/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES007784/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA054281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95171/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA063464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL54473/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC048047/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL072518/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL088215/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007092/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055018/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR010284/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL053934/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL063429/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085084/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG020098/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HL100245/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087698-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK089256/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95172/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059684/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA140388/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC048050/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-72991/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85079/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01AG62103/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055022/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL054473/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95100/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97072/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-45133/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01AG62106/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL054495/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 32122/PHS HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97058/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL054496/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL054471/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL54495/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL053937/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85239/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-48048/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR017696/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-72996/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC075150/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55018/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01- HL-071051/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG028321/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG-023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095171/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 2M01RR010284/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 44221/PHS HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97061/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC065226/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027058/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000080/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC045133/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087700/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-73004/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 32111-13/PHS HHS/United States
- # Z01-AG000513/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95170/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL054495/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-72998/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071258/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA054281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL54471/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL54509/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC035129/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL055673/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37-CA54281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97069/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL054473/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA098663/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30-ES10126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HL54472/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-550190/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-65226/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004726/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA100598/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

