Cellular trafficking of thymosin beta-4 in HEPG2 cells following serum starvation
- PMID: 23967050
- PMCID: PMC3743897
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067999
Cellular trafficking of thymosin beta-4 in HEPG2 cells following serum starvation
Abstract
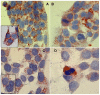
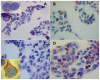
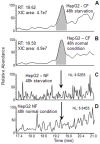
Thymosin beta-4 (Tβ4) is an ubiquitous multi-functional regenerative peptide, related to many critical biological processes, with a dynamic and flexible conformation which may influence its functions and its subcellular distribution. For these reasons, the intracellular localization and trafficking of Tβ4 is still not completely defined and is still under investigation in in vivo as well as in vitro studies. In the current study we used HepG2 cells, a human hepatoma cell line; cells growing in normal conditions with fetal bovine serum expressed high levels of Tβ4, restricted to the cytoplasm until 72 h. At 84 h, a diffuse Tβ4 cytoplasmic immunostaining shifted to a focal perinuclear and nuclear reactivity. In the absence of serum, nuclear reactivity was localized in small granules, evenly dispersed throughout the entire nuclear envelop, and was observed as earlier as at 48 h. Cytoplasmic immunostaining for Tβ4 in HepG2 cells under starvation appeared significantly lower at 48 h and decreased progressively at 72 and at 84 h. At these time points, the decrease in cytoplasmic staining was associated with a progressive increase in nuclear reactivity, suggesting a possible translocation of the peptide from the cytoplasm to the nuclear membrane. The normal immunocytochemical pattern was restored when culture cells submitted to starvation for 84 h received a new complete medium for 48 h. Mass spectrometry analysis, performed on the nuclear and cytosolic fractions of HepG2 growing with and without serum, showed that Tβ4 was detectable only in the cytosolic and not in the intranuclear fraction. These data suggest that Tβ4 is able to translocate from different cytoplasmic domains to the nuclear membrane and back, based on different stress conditions within the cell. The punctuate pattern of nuclear Tβ4 immunostaining associated with Tβ4 absence in the nucleoplasm suggest that this peptide might be localized in the nuclear pores, where it could regulate the pore permeability.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Thymosin β4 cytoplasmic/nuclear translocation as a new marker of cellular stress. A Caco2 case study.RSC Adv. 2020 Mar 30;10(21):12680-12688. doi: 10.1039/c9ra10365a. eCollection 2020 Mar 24. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35497634 Free PMC article.
-
Thymosin beta 4 may translocate from the cytoplasm in to the nucleus in HepG2 cells following serum starvation. An ultrastructural study.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 2;10(3):e0119642. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119642. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25835495 Free PMC article.
-
Ku80 as a novel receptor for thymosin beta4 that mediates its intracellular activity different from G-actin sequestering.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jan 18;283(3):1534-1544. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M707539200. Epub 2007 Nov 4. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 17984099
-
Potential role of thymosin Beta 4 in liver fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 May 8;16(5):10624-35. doi: 10.3390/ijms160510624. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26006229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thymosin beta4 in multiple myeloma: friend or foe.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Apr;1194:125-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05470.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20536459 Review.
Cited by
-
Thymosin β4 cytoplasmic/nuclear translocation as a new marker of cellular stress. A Caco2 case study.RSC Adv. 2020 Mar 30;10(21):12680-12688. doi: 10.1039/c9ra10365a. eCollection 2020 Mar 24. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35497634 Free PMC article.
-
Toward the renal vesicle: Ultrastructural investigation of the cap mesenchyme splitting process in the developing kidney.J Public Health Res. 2022 Oct 24;11(4):22799036221124076. doi: 10.1177/22799036221124076. eCollection 2022 Oct. J Public Health Res. 2022. PMID: 36310827 Free PMC article.
-
Thymosin β4 and β10 Expression in Human Organs during Development: A Review.Cells. 2024 Jun 27;13(13):1115. doi: 10.3390/cells13131115. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38994967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thymosin beta-4 regulates activation of hepatic stellate cells via hedgehog signaling.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 19;7(1):3815. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03782-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28630423 Free PMC article.
-
Thymosin beta 4 may translocate from the cytoplasm in to the nucleus in HepG2 cells following serum starvation. An ultrastructural study.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 2;10(3):e0119642. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119642. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25835495 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ballweber E, Hannappel E, Huff T, Stephan H, Haener M, et al. (2002) Polymerization of chemically cross-linked actin:thymosin beta(4) complex to filamentous actin: alteration in helical parameters and visualization of thymosin beta(4) binding on F-actin. J Mol Biol 315: 613–625. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein AL, Hannappel E, Sosne G, Kleinman HK (2012) Thymosin β4: a multi-functional regenerative peptide. Basic properties and clinical applications. Expert Opin Biol Ther 12: 37–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

