Aureolib - a proteome signature library: towards an understanding of staphylococcus aureus pathophysiology
- PMID: 23967085
- PMCID: PMC3742771
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070669
Aureolib - a proteome signature library: towards an understanding of staphylococcus aureus pathophysiology
Abstract
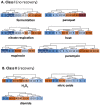
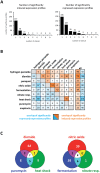
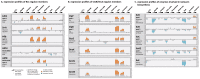
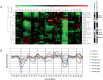
Gel-based proteomics is a powerful approach to study the physiology of Staphylococcus aureus under various growth restricting conditions. We analyzed 679 protein spots from a reference 2-dimensional gel of cytosolic proteins of S. aureus COL by mass spectrometry resulting in 521 different proteins. 4,692 time dependent protein synthesis profiles were generated by exposing S. aureus to nine infection-related stress and starvation stimuli (H2O2, diamide, paraquat, NO, fermentation, nitrate respiration, heat shock, puromycin, mupirocin). These expression profiles are stored in an online resource called Aureolib (http://www.aureolib.de). Moreover, information on target genes of 75 regulators and regulatory elements were included in the database. Cross-comparisons of this extensive data collection of protein synthesis profiles using the tools implemented in Aureolib lead to the identification of stress and starvation specific marker proteins. Altogether, 226 protein synthesis profiles showed induction ratios of 2.5-fold or higher under at least one of the tested conditions with 157 protein synthesis profiles specifically induced in response to a single stimulus. The respective proteins might serve as marker proteins for the corresponding stimulus. By contrast, proteins whose synthesis was increased or repressed in response to more than four stimuli are rather exceptional. The only protein that was induced by six stimuli is the universal stress protein SACOL1759. Most strikingly, cluster analyses of synthesis profiles of proteins differentially synthesized under at least one condition revealed only in rare cases a grouping that correlated with known regulon structures. The most prominent examples are the GapR, Rex, and CtsR regulon. In contrast, protein synthesis profiles of proteins belonging to the CodY and σ(B) regulon are widely distributed. In summary, Aureolib is by far the most comprehensive protein expression database for S. aureus and provides an essential tool to decipher more complex adaptation processes in S. aureus during host pathogen interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Characterization of the sigma(B) regulon in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 2000 Dec;182(24):6983-91. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.24.6983-6991.2000. J Bacteriol. 2000. PMID: 11092859 Free PMC article.
-
Protecs, a comprehensive and powerful storage and analysis system for OMICS data, applied for profiling the anaerobiosis response of Staphylococcus aureus COL.Proteomics. 2010 Aug;10(16):2982-3000. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200900388. Proteomics. 2010. PMID: 20662099
-
Comparative proteomics of Staphylococcus aureus and the response of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-sensitive strains to Triton X-100.Microbiology (Reading). 2002 Sep;148(Pt 9):2765-2781. doi: 10.1099/00221287-148-9-2765. Microbiology (Reading). 2002. PMID: 12213923
-
From the genome sequence via the proteome to cell physiology - Pathoproteomics and pathophysiology of Staphylococcus aureus.Int J Med Microbiol. 2018 Aug;308(6):545-557. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2018.01.002. Epub 2018 Jan 5. Int J Med Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29398252 Review.
-
Physiological proteomics and stress/starvation responses in Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus.Res Microbiol. 2009 May;160(4):245-58. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2009.03.008. Epub 2009 May 3. Res Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19403106 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic Signatures of Clostridium difficile Stressed with Metronidazole, Vancomycin, or Fidaxomicin.Cells. 2018 Nov 15;7(11):213. doi: 10.3390/cells7110213. Cells. 2018. PMID: 30445773 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Enterococcus faecalis small RNAs in stress response and virulence.Infect Immun. 2014 Sep;82(9):3599-611. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01900-14. Epub 2014 Jun 9. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24914223 Free PMC article.
-
A global Staphylococcus aureus proteome resource applied to the in vivo characterization of host-pathogen interactions.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 8;7(1):9718. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10059-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28887440 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptation of Dinoroseobacter shibae to oxidative stress and the specific role of RirA.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 29;16(3):e0248865. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248865. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33780465 Free PMC article.
-
Application and Perspectives of MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry in Clinical Microbiology Laboratories.Microorganisms. 2021 Jul 20;9(7):1539. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9071539. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34361974 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Deresinski S (2005) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: an evolutionary, epidemiologic, and therapeutic odyssey. Clin Infect Dis 40: 562–573. - PubMed
-
- Plata K, Rosato AE, Wegrzyn G (2009) Staphylococcus aureus as an infectious agent: overview of biochemistry and molecular genetics of its pathogenicity. Acta Biochim Pol 56: 597–612. - PubMed
-
- Ziebandt AK, Kusch H, Degner M, Jaglitz S, Sibbald MJ, et al. (2010) Proteomics uncovers extreme heterogeneity in the Staphylococcus aureus exoproteome due to genomic plasticity and variant gene regulation. Proteomics 10: 1634–1644. - PubMed
-
- Richardson AR, Libby SJ, Fang FC (2008) A nitric oxide-inducible lactate dehydrogenase enables Staphylococcus aureus to resist innate immunity. Science 319: 1672–1676. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

