Identification of potential Plk1 targets in a cell-cycle specific proteome through structural dynamics of kinase and Polo box-mediated interactions
- PMID: 23967120
- PMCID: PMC3744538
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070843
Identification of potential Plk1 targets in a cell-cycle specific proteome through structural dynamics of kinase and Polo box-mediated interactions
Abstract
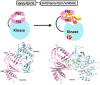
Polo like kinase 1 (Plk1) is a key player in orchestrating the wide variety of cell-cycle events ranging from centrosome maturation, mitotic entry, checkpoint recovery, transcriptional control, spindle assembly, mitotic progression, cytokinesis and DNA damage checkpoints recovery. Due to its versatile nature, Plk1 is considered an imperative regulator to tightly control the diverse aspects of the cell cycle network. Interactions among Plk1 polo box domain (PBD) and its putative binding proteins are crucial for the activation of Plk1 kinase domain (KD). To date, only a few substrate candidates have been characterized through the inclusion of both polo box and kinase domain-mediated interactions. Thus it became compelling to explore precise and specific Plk1 substrates through reassessment and extension of the structure-function paradigm. To narrow this apparently wide gap in knowledge, here we employed a thorough sequence search of Plk1 phosphorylation signature containing proteins and explored their structure-based features like conceptual PBD-binding capabilities and subsequent recruitment of KD directed phosphorylation to dissect novel targets of Plk1. Collectively, we identified 4,521 phosphodependent proteins sharing similarity to the consensus phosphorylation and PBD recognition motifs. Subsequent application of filters including similarity index, Gene Ontology enrichment and protein localization resulted in stringent pre-filtering of irrelevant candidates and isolated unique targets with well-defined roles in cell-cycle machinery and carcinogenesis. These candidates were further refined structurally using molecular docking and dynamic simulation assays. Overall, our screening approach enables the identification of several undefined cell-cycle associated functions of Plk1 by uncovering novel phosphorylation targets.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Barr FA, Sillje HH, Nigg EA (2004) Polo-like kinases and the orchestration of cell division. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5: 429–440. - PubMed
-
- Glover DM (2005) Polo kinase and progression through M phase in Drosophila: a perspective from the spindle poles. Oncogene 24: 230–237. - PubMed
-
- van de Weerdt BC, Medema RH (2006) Polo-like kinases: a team in control of the division. Cell Cycle 5: 853–864. - PubMed
-
- Llamazares S, Moreira A, Tavares A, Girdham C, Spruce BA, et al. (1991) polo encodes a protein kinase homolog required for mitosis in Drosophila. Genes Dev 5: 2153–2165. - PubMed
-
- Sunkel CE, Glover DM (1988) Polo, a mitotic mutant of Drosophila displaying abnormal spindle poles. J Cell Sci 89: 25–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

