Shizukaol D isolated from Chloranthus japonicas inhibits AMPK-dependent lipid content in hepatic cells by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction
- PMID: 23967345
- PMCID: PMC3743771
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073527
Shizukaol D isolated from Chloranthus japonicas inhibits AMPK-dependent lipid content in hepatic cells by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction
Abstract
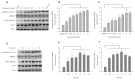
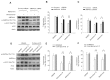
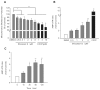
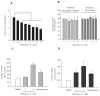
This study is the first to demonstrate that shizukaol D, a natural compound isolated from Chloranthusjaponicus, can activate AMP- activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key sensor and regulator of intracellular energy metabolism, leading to a decrease in triglyceride and cholesterol levels in HepG2 cells. Furthermore, we found that shizukaol D induces mitochondrial dysfunction by depolarizing the mitochondrial membrane and suppressing energy production, which may result in AMPK activation. Our results provide a possible link between mitochondrial dysfunction and AMPK activation and suggest that shizukaol D might be used to treat metabolic syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Carling D (2004) The AMP-activated protein kinase cascade--a unifying system for energy control. Trends Biochem Sci 29: 18-24. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2003.11.005. PubMed: 14729328. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hardie DG (2004) The AMP-activated protein kinase pathway--new players upstream and downstream. J Cell Sci 117: 5479-5487. doi:10.1242/jcs.01540. PubMed: 15509864. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hawley SA, Fullerton MD, Ross FA, Schertzer JD, Chevtzoff C et al. (2012) The ancient drug salicylate directly activates AMP-activated protein kinase. Science 336: 918-922. doi:10.1126/science.1215327. PubMed: 22517326. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fujii N, Hayashi T, Hirshman MF, Smith JT, Habinowski SA et al. (2000) Exercise induces isoform-specific increase in 5'AMP-activated protein kinase activity in human skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 273: 1150-1155. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2000.3073. PubMed: 10891387. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hardie DG, Scott JW, Pan DA, Hudson ER (2003) Management of cellular energy by the AMP-activated protein kinase system. FEBS Lett 546: 113-120. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(03)00560-X. PubMed: 12829246. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

