SAMP8 mice have altered hippocampal gene expression in long term potentiation, phosphatidylinositol signaling, and endocytosis pathways
- PMID: 23969180
- PMCID: PMC3839577
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.07.018
SAMP8 mice have altered hippocampal gene expression in long term potentiation, phosphatidylinositol signaling, and endocytosis pathways
Abstract
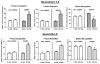
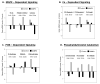
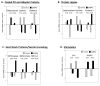
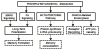
The senescence-accelerated mouse (SAMP8) strain exhibits decreased learning and memory and increased amyloid beta (Aβ) peptide accumulation at 12 months. To detect differences in gene expression in SAMP8 mice, we used a control mouse that was a 50% cross between SAMP8 and CD-1 mice and which showed no memory deficits (50% SAMs). We then compared gene expression in the hippocampus of 4- and 12-month-old SAMP8 and control mice using Affymetrix gene arrays. At 12 months, but not at 4 months, pathway analysis revealed significant differences in the long term potentiation (6 genes), phosphatidylinositol signaling (6 genes), and endocytosis (10 genes) pathways. The changes in long term potentiation included mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling (N-ras, cAMP responsive element binding protein [CREB], protein phosphatase inhibitor 1) and Ca-dependent signaling (inositol triphosphate [ITP] receptors 1 and 2 and phospholipase C). Changes in phosphatidylinositol signaling genes suggested altered signaling through phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase, and Western blotting revealed phosphorylation changes in serine/threonine protein kinase AKT and 70S6K. Changes in the endocytosis pathway involved genes related to clathrin-mediated endocytosis (dynamin and clathrin). Endocytosis is required for receptor recycling, is involved in Aβ metabolism, and is regulated by phosphatidylinositol signaling. In summary, these studies demonstrate altered gene expression in 3 SAMP8 hippocampal pathways associated with memory formation and consolidation. These pathways might provide new therapeutic targets in addition to targeting Aβ metabolism itself.
Keywords: Clathrin-mediated endocytosis; Hippocampal gene expression; Long term potentiation; Memory loss; Phosphatidylinositol signaling; SAMP8 mouse.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Alvarez-Lopez MJ, Castro-Freire M, Cosin-Tomas M, Sanchez-Roige S, Lalanza JF, del Valle J, Parrizas M, Camins A, Pallas M, Escorihuela RM, Kaliman P. Long-term exercise modulates hippocampal gene expression in senescent female mice. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013;33:1177–1190. - PubMed
-
- Balleza-Tapia H, Pena F. Pharmacology of the intracellular pathways activated by amyloid beta protein. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2009;9:724–740. - PubMed
-
- Blitzer RD, Connor JH, Brown GP, Wong T, Shenolikar S, Iyengar R, Landau EM. Gating of CaMKII by cAMP-regulated protein phosphatase activity during LTP. Science. 1998;280:1940–1942. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

