Molecular validation of the schizophrenia spectrum
- PMID: 23970557
- PMCID: PMC3885304
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbt122
Molecular validation of the schizophrenia spectrum
Abstract
Background: Early descriptive work and controlled family and adoption studies support the hypothesis that a range of personality and nonschizophrenic psychotic disorders aggregate in families of schizophrenic probands. Can we validate, using molecular polygene scores from genome-wide association studies (GWAS), this schizophrenia spectrum?
Methods: The predictive value of polygenic findings reported by the Psychiatric GWAS Consortium (PGC) was applied to 4 groups of relatives from the Irish Study of High-Density Schizophrenia Families (ISHDSF; N = 836) differing on their assignment within the schizophrenia spectrum. Genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphism data for affected and unaffected relatives were used to construct per-individual polygene risk scores based on the PGC stage-I results. We compared mean polygene scores in the ISHDSF with mean scores in ethnically matched population controls (N = 929).
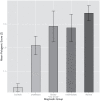
Results: The schizophrenia polygene score differed significantly across diagnostic categories and was highest in those with narrow schizophrenia spectrum, lowest in those with no psychiatric illness, and in-between in those classified in the intermediate, broad, and very broad schizophrenia spectrum. Relatives of all of these groups of affected subjects, including those with no diagnosis, had schizophrenia polygene scores significantly higher than the control sample.
Conclusions: In the relatives of high-density families, the observed pattern of enrichment of molecular indices of schizophrenia risk suggests an underlying, continuous liability distribution and validates, using aggregate common risk alleles, a genetic basis for the schizophrenia spectrum disorders. In addition, as predicted by genetic theory, nonpsychotic members of multiply-affected schizophrenia families are significantly enriched for replicated, polygenic risk variants compared with the general population.
Keywords: GWAS; polygene score; schizophrenia; schizophrenia spectrum.
Figures
References
-
- Kraepelin E. Dementia Praecox and Paraphrenia. Huntington, NY: Krieger Publishing; 1971.
-
- Bleuler E. Dementia Praecox, or The Group of Schizophrenias. New York, NY: International Universities Press; 1950.
-
- Kendler KS. Diagnostic approaches to schizotypal personality disorder: a historical perspective. Schizophr Bull. 1985;11:538–553 - PubMed
-
- Zerbin-Rudin E, Kendler KS. Ernst Rudin (1874-1952) and his genealogic-demographic department in Munich (1917-1986): an introduction to their family studies of schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet. 1996;67:332–337 - PubMed
-
- Kallmann FJ. The Genetics of Schizophrenia. New York, NY: J.S. Augustin; 1938.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical