The epidemiology of HIV infection in Morocco: systematic review and data synthesis
- PMID: 23970764
- PMCID: PMC3764773
- DOI: 10.1177/0956462413477971
The epidemiology of HIV infection in Morocco: systematic review and data synthesis
Abstract
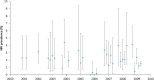
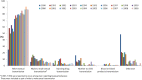
Morocco has made significant strides in building its HIV research capacity. Based on a wealth of empirical data, the objective of this study was to conduct a comprehensive and systematic literature review and analytical synthesis of HIV epidemiological evidence in this country. Data were retrieved using three major sources of literature and data. HIV transmission dynamics were found to be focused in high-risk populations, with female sex workers (FSWs) and clients contributing the largest share of new HIV infections. There is a pattern of emerging epidemics among some high-risk populations, and some epidemics, particularly among FSWs, appear to be established and stable. The scale of the local HIV epidemics and populations affected show highly heterogeneous geographical distribution. To optimize the national HIV response, surveillance and prevention efforts need to be expanded among high-risk populations and in geographic settings where low intensity and possibly concentrated HIV epidemics are emerging or are already endemic.
Keywords: AIDS; HIV; Morocco; Review; epidemiology; prevalence; sexually transmitted infection.
Figures

References
-
- Clock OMP. Official Moroccan Population Clock.
-
- Abu-Raddad LJ, Hilmi N, Mumtaz G, et al. Epidemiology of HIV infection in the Middle East and North Africa. AIDS 2010;24(Suppl. 2):S5–23 - PubMed
-
- Abu-Raddad L, Akala FA, Semini I, Riedner G, Wilson D, Tawil O. Characterizing the HIV/AIDS Epidemic in the Middle East and North Africa: Time for Strategic Action. Middle East and North Africa HIV/AIDS Epidemiology Synthesis Project. World Bank/UNAIDS/WHO Publication. Washington DC: The World Bank Press, 2010
-
- Mumtaz G, Hilmi N, Zidouh A, et al. 2010. HIV modes of transmission analysis in Morocco. Kingdom of Morocco Ministry of Health and National STI/AIDS Programme, Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS, and Weill Cornell Medical College – Qatar.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

