Estrogen receptor negative/progesterone receptor positive breast cancer is not a reproducible subtype
- PMID: 23971947
- PMCID: PMC3978610
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr3462
Estrogen receptor negative/progesterone receptor positive breast cancer is not a reproducible subtype
Abstract
Introduction: Estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) testing are performed in the evaluation of breast cancer. While the clinical utility of ER as a predictive biomarker to identify patients likely to benefit from hormonal therapy is well-established, the added value of PR is less well-defined. The primary goals of our study were to assess the distribution, inter-assay reproducibility, and prognostic significance of breast cancer subtypes defined by patterns of ER and PR expression.
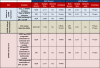
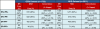
Methods: We integrated gene expression microarray (GEM) and clinico-pathologic data from 20 published studies to determine the frequency (n = 4,111) and inter-assay reproducibility (n = 1,752) of ER/PR subtypes (ER+/PR+, ER+/PR-, ER-/PR-, ER-/PR+). To extend our findings, we utilized a cohort of patients from the Nurses' Health Study (NHS) with ER/PR data recorded in the medical record and assessed on tissue microarrays (n = 2,011). In both datasets, we assessed the association of ER and PR expression with survival.
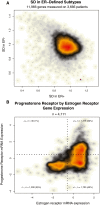
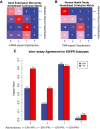
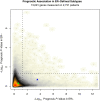
Results: In a genome-wide analysis, progesterone receptor was among the least variable genes in ER- breast cancer. The ER-/PR+ subtype was rare (approximately 1 to 4%) and showed no significant reproducibility (Kappa = 0.02 and 0.06, in the GEM and NHS datasets, respectively). The vast majority of patients classified as ER-/PR+ in the medical record (97% and 94%, in the GEM and NHS datasets) were re-classified by a second method. In the GEM dataset (n = 2,731), progesterone receptor mRNA expression was associated with prognosis in ER+ breast cancer (adjusted P <0.001), but not in ER- breast cancer (adjusted P = 0.21). PR protein expression did not contribute significant prognostic information to multivariate models considering ER and other standard clinico-pathologic features in the GEM or NHS datasets.
Conclusion: ER-/PR+ breast cancer is not a reproducible subtype. PR expression is not associated with prognosis in ER- breast cancer, and PR does not contribute significant independent prognostic information to multivariate models considering ER and other standard clinico-pathologic factors. Given that PR provides no clinically actionable information in ER+ breast cancer, these findings question the utility of routine PR testing in breast cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Hammond ME, Hayes DF, Dowsett M, Allred DC, Hagerty KL, Badve S, Fitzgibbons PL, Francis G, Goldstein NS, Hayes M, Hicks DG, Lester S, Love R, Mangu PB, McShane L, Miller K, Osborne CK, Paik S, Perlmutter J, Rhodes A, Sasano H, Schwartz JN, Sweep FC, Taube S, Torlakovic EE, Valenstein P, Viale G, Visscher D, Wheeler T, Williams RB. et al.American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;15:2784–2795. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.25.6529. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

