Enhancing microvascular formation and vessel maturation through temporal control over multiple pro-angiogenic and pro-maturation factors
- PMID: 23972477
- PMCID: PMC3811005
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.08.007
Enhancing microvascular formation and vessel maturation through temporal control over multiple pro-angiogenic and pro-maturation factors
Abstract
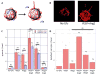
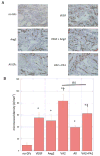
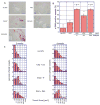
Therapeutic stimulation of angiogenesis to re-establish blood flow in ischemic tissues offers great promise as a treatment for patients suffering from cardiovascular disease or trauma. Since angiogenesis is a complex, multi-step process, different signals may need to be delivered at appropriate times in order to promote a robust and mature vasculature. The effects of temporally regulated presentation of pro-angiogenic and pro-maturation factors were investigated in vitro and in vivo in this study. Pro-angiogenic factors vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and angiopoietin 2 (Ang2) cooperatively promoted endothelial sprouting and pericyte detachment in a three-dimensional in vitro EC-pericyte co-culture model. Pro-maturation factors platelet-derived growth factor B (PDGF) and angiopoietin 1 (Ang1) inhibited the early stages of VEGF- and Ang2-mediated angiogenesis if present simultaneously with VEGF and Ang2, but promoted these behaviors if added subsequently to the pro-angiogenesis factors. VEGF and Ang2 were also found to additively enhance microvessel density in a subcutaneous model of blood vessel formation, while simultaneously administered PDGF/Ang1 inhibited microvessel formation. However, a temporally controlled scaffold that released PDGF and Ang1 at a delay relative to VEGF/Ang2 promoted both vessel maturation and vascular remodeling without inhibiting sprouting angiogenesis. Our results demonstrate the importance of temporal control over signaling in promoting vascular growth, vessel maturation and vascular remodeling. Delivering multiple growth factors in combination and sequence could aid in creating tissue engineered constructs and therapies aimed at promoting healing after acute wounds and in chronic conditions such as diabetic ulcers and peripheral artery disease.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Controlled drug release; Drug delivery; Endothelial cell; Growth factors; Smooth muscle cell.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Attanasio S, Snell J. Therapeutic angiogenesis in the management of critical limb ischemia: current concepts and review. Cardiol Rev. 2009;17:115–20. - PubMed
-
- Freedman S, Isner J. Therapeutic angiogenesis for ischemic cardiovascular disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2001;33:379–93. - PubMed
-
- Losordo D, Dimmeler S. Therapeutic angiogenesis and vasculogenesis for ischemic disease: part II: cell-based therapies. Circulation. 2004;109:2692–7. - PubMed
-
- Silva E, Mooney D. Spatiotemporal control of vascular endothelial growth factor delivery from injectable hydrogels enhances angiogenesis. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5:590–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

