Developmental continuity of oppositional defiant disorder subdimensions at ages 8, 10, and 13 years and their distinct psychiatric outcomes at age 16 years
- PMID: 23972698
- PMCID: PMC4026040
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaac.2013.06.013
Developmental continuity of oppositional defiant disorder subdimensions at ages 8, 10, and 13 years and their distinct psychiatric outcomes at age 16 years
Abstract
Objective: To test the developmental continuity, interrelationships, and predictive associations of the oppositional defiant disorder (ODD) subdimensions of irritable, headstrong, and hurtful.
Method: Data were collected from 6,328 mother-child pairs participating in the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (United Kingdom).
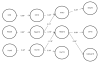
Results: Developmental continuity for each subdimension was strong and interrelationships indicated that headstrong was associated mainly with irritable, whereas irritable did not cross associate with other ODD subdimensions; and hurtful was associated with lower levels of headstrong. With regard to associations at age 16 years, irritable at age 13 years was associated with depression, whereas headstrong at 13 was associated with delinquency and callous attitude; at age 13, hurtful failed to associate with any of the 3 age 16 outcomes.
Conclusions: The results suggest that the ODD headstrong and irritable subdimensions are developmentally distinct, with small cross-over (i.e., headstrong to irritable), and are associated with unique outcomes. Hurtful does not appear to be associated with future maladjustment in children.
Keywords: Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC); callous traits; conduct problems; depression; oppositional defiant disorder.
Copyright © 2013 American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Angold A, Costello EJ, Erlanki A. Comorbidity. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1999;40:57–87. - PubMed
-
- Loeber R, Green SM, Keenan K, Lahey BB. Which boys will fare worse? Early predictors of the onset of conduct disorder in a six-year longitudinal study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1995;34:499–509. - PubMed
-
- Maughan B, Rowe R, Messer J, Goodman R, Meltzer H. Conduct disorder and oppositional defiant disorder in a national sample: developmental epidemiology. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2004;45:609–621. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

