The effect of restaging transurethral resection on recurrence and progression rates in patients with nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer treated with intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guérin
- PMID: 23973518
- PMCID: PMC4157345
- DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.08.022
The effect of restaging transurethral resection on recurrence and progression rates in patients with nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer treated with intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guérin
Abstract
Purpose: We determined whether restaging resection before initiating induction intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guérin improves the recurrence-free rate in patients with high risk nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer.
Materials and methods: We retrospectively analyzed data on 1,021 patients treated at our institution with intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guérin for nonmuscle invasive high risk bladder cancer. All patients underwent a second resection except those already receiving bacillus Calmette-Guérin at the time of initial consultation and those who refused restaging resection. All patients were assessed every 3 to 12 months for a minimum of 5 years. Univariate and multivariate regression was used to identify predictors of 5-year recurrence.
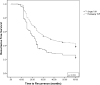
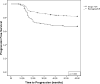
Results: Restaging transurethral resection was performed in 894 patients (87.5%). At restaging resection viable tumor was found in 496 patients (55.5%). At 3 months patients with a single resection had a 44.3% recurrence rate compared to 9.6% in those with restaging resection (p <0.01). On multivariate analysis a single transurethral resection was the only predictor of recurrence at 5 years (OR 2.1, 95% CI 1.3-3.3, p = 0.01). Time to recurrence in patients with a single resection was significantly shorter than in those with restaging resection (median 22 vs 36 months, p <0.001).
Conclusions: Failure to repeat resection before initiating intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guérin therapy for high risk nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer significantly increases the risk of recurrence. Therefore, we believe that restaging resection should be performed before initiating bacillus Calmette-Guérin therapy in all patients with high risk nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer.
Keywords: BCG; BCG vaccine; CIS; NMIBC; TUR; bacillus Calmette-Guérin; carcinoma; carcinoma in situ; local; neoplasm recurrence; nonmuscle invasive bladder carcinoma; reoperation; transurethral resection; urinary bladder.
Copyright © 2014 American Urological Association Education and Research, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Words of wisdom. Re: The effect of restaging transurethral resection on recurrence and progression rates in patients with nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer treated with intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin.Eur Urol. 2015 Apr;67(4):815. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.12.050. Eur Urol. 2015. PMID: 25765211 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lamm DL, Thor DE, Harris SC, et al. Bacillus Calmette-Guerin immunotherapy of superficial bladder cancer. J Urol. 1980;124:38. - PubMed
-
- Herr HW, Pinsky CM, Whitmore WF, Jr, et al. Effect of intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) on carcinoma in situ of the bladder. Cancer. 1983;51:1323. - PubMed
-
- Lamm DL, Blumenstein BA, Crawford ED, et al. A randomized trial of intravesical doxorubicin and immunotherapy with bacille Calmette-Guerin for transitional-cell carcinoma of the bladder. N Engl J Med. 1991;325:1205. - PubMed
-
- Malmstrom PU, Wijkstrom H, Lundholm C, et al. 5-year followup of a randomized prospective study comparing mitomycin C and bacillus Calmette-Guerin in patients with superficial bladder carcinoma. Swedish-Norwegian Bladder Cancer Study Group. J Urol. 1999;161:1124. - PubMed
-
- Babjuk M, Oosterlinck W, Sylvester R, et al. EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder, the 2011 update. Eur Urol. 2011;59:997. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

