Independent prognostic value of BCR-ABL1-like signature and IKZF1 deletion, but not high CRLF2 expression, in children with B-cell precursor ALL
- PMID: 23974192
- PMCID: PMC3795461
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-10-462358
Independent prognostic value of BCR-ABL1-like signature and IKZF1 deletion, but not high CRLF2 expression, in children with B-cell precursor ALL
Abstract
Most relapses in childhood B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL) are not predicted using current prognostic features. Here, we determined the co-occurrence and independent prognostic relevance of 3 recently identified prognostic features: BCR-ABL1-like gene signature, deletions in IKZF1, and high CRLF2 messenger RNA expression (CRLF2-high). These features were determined in 4 trials representing 1128 children with ALL: DCOG ALL-8, ALL9, ALL10, and Cooperative ALL (COALL)-97/03. BCR-ABL1-like, IKZF1-deleted, and CRLF2-high cases constitute 33.7% of BCR-ABL1-negative, MLL wild-type BCP-ALL cases, of which BCR-ABL1-like and IKZF1 deletion (co)occurred most frequently. Higher cumulative incidence of relapse was found for BCR-ABL1-like and IKZF1-deleted, but not CRLF2-high, cases relative to remaining BCP-ALL cases, reflecting the observations in each of the cohorts analyzed separately. No relapses occurred among cases with CRLF2-high as single feature, whereas 62.9% of all relapses in BCR-ABL1-negative, MLL wild-type BCP-ALL occurred in cases with BCR-ABL1-like signature and/or IKZF1 deletion. Both the BCR-ABL1-like signature and IKZF1 deletions were prognostic features independent of conventional prognostic markers in a multivariate model, and both remained prognostic among cases with intermediate minimal residual disease. The BCR-ABL1-like signature and an IKZF1 deletion, but not CRLF2-high, are prognostic factors and are clinically of importance to identify high-risk patients who require more intensive and/or alternative therapies.
Figures

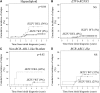
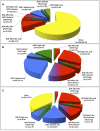

Comment in
-
Therapy of pediatric ALL: from Bowie to Obama.Blood. 2013 Oct 10;122(15):2531-2. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-09-523688. Blood. 2013. PMID: 24113793 No abstract available.
References
-
- Möricke A, Zimmermann M, Reiter A, et al. Long-term results of five consecutive trials in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia performed by the ALL-BFM study group from 1981 to 2000. Leukemia. 2010;24(2):265–284. - PubMed
-
- Kuiper RP, Waanders E, van der Velden VHJ, et al. IKZF1 deletions predict relapse in uniformly treated pediatric precursor B-ALL. Leukemia. 2010;24(7):1258–1264. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

