Intertester agreement in refractive error measurements
- PMID: 23974664
- PMCID: PMC3894690
- DOI: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000000025
Intertester agreement in refractive error measurements
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the intertester agreement of refractive error measurements between lay and nurse screeners using the Retinomax Autorefractor and the SureSight Vision Screener.
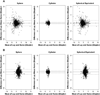
Methods: Trained lay and nurse screeners measured refractive error in 1452 preschoolers (3 to 5 years old) using the Retinomax and the SureSight in a random order for screeners and instruments. Intertester agreement between lay and nurse screeners was assessed for sphere, cylinder, and spherical equivalent (SE) using the mean difference and the 95% limits of agreement. The mean intertester difference (lay minus nurse) was compared between groups defined based on the child's age, cycloplegic refractive error, and the reading's confidence number using analysis of variance. The limits of agreement were compared between groups using the Brown-Forsythe test. Intereye correlation was accounted for in all analyses.
Results: The mean intertester differences (95% limits of agreement) were -0.04 (-1.63, 1.54) diopter (D) sphere, 0.00 (-0.52, 0.51) D cylinder, and -0.04 (1.65, 1.56) D SE for the Retinomax and 0.05 (-1.48, 1.58) D sphere, 0.01 (-0.58, 0.60) D cylinder, and 0.06 (-1.45, 1.57) D SE for the SureSight. For either instrument, the mean intertester differences in sphere and SE did not differ by the child's age, cycloplegic refractive error, or the reading's confidence number. However, for both instruments, the limits of agreement were wider when eyes had significant refractive error or the reading's confidence number was below the manufacturer's recommended value.
Conclusions: Among Head Start preschool children, trained lay and nurse screeners agree well in measuring refractive error using the Retinomax or the SureSight. Both instruments had similar intertester agreement in refractive error measurements independent of the child's age. Significant refractive error and a reading with low confidence number were associated with worse intertester agreement.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None.
Figures


References
-
- Schmidt P, Maguire M, Dobson V, Quinn G, Ciner E, Cyert L, Kulp MT, Moore B, Orel-Bixler D, Redford M, Ying GS. Comparison of preschool vision screening tests as administered by licensed eye care professionals in the Vision In Preschoolers Study. Vision In Preschoolers (VIP) Study Group. Ophthalmology. 2004;111:637–650. - PubMed
-
- Vision In Preschoolers (VIP) Study Group. Preschool vision screening tests administered by nurse screeners compared to lay screeners in the Vision in Preschoolers Study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005;46:2639–2648. - PubMed
-
- Cordonnier M, De Maertelaer V. Comparison between two hand-held autorefractors: the SureSight and the Retinomax. Strabismus. 2004;12:261–274. - PubMed
-
- Paff T, Oudesluys-Murphy AM, Wolterbeek R, Swart-van den Berg M, de Nie JM, Tijssen E, Schalij-Delfos NE. Screening for refractive errors in children: the plusoptiX S08 and the Retinomax K-plus2 performed by a lay screener compared to cycloplegic retinoscopy. J AAPOS. 2010;14:478–483. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U10EY12534/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY012545/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EY018908/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U10EY12545/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY012647/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U10EY12547/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY012648/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY012550/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U10EY12550/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY012644/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY012534/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R21EY018908/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U10EY12644/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U10EY12648/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U10EY12647/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY012547/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

