Sarcopenic obesity: how do we treat it?
- PMID: 23974769
- PMCID: PMC4046899
- DOI: 10.1097/01.med.0000433071.11466.7f
Sarcopenic obesity: how do we treat it?
Abstract
Purpose of review: The increasing prevalence of sarcopenic obesity in older adults has heightened interest in identifying the most effective treatment. This review highlights recent progress in the management, with an emphasis on lifestyle interventions and pharmacologic therapy aimed at reversing sarcopenic obesity.
Recent findings: Whereas weight loss and exercise independently reverse sarcopenic obesity, they act synergistically in combination to improve body composition and physical function, beyond which is observed with either intervention alone. Optimizing protein intake appears to have beneficial effects on net muscle protein accretion in older adults. Myostatin inhibition is associated with favorable changes in body composition in animal studies, although experience in humans is relatively limited. Testosterone and growth hormone offer improvements in body composition, but the benefits must be weighed against potential risks of therapy. GHRH-analog therapy shows promise, but further studies are needed in older adults.
Summary: At present, lifestyle interventions incorporating both diet-induced weight loss and regular exercise appear to be the optimal treatment for sarcopenic obesity. Maintenance of adequate protein intake is also advisable. Ongoing studies will determine whether pharmacologic therapy such as myostatin inhibitors or GHRH analogs have a role in the treatment of sarcopenic obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
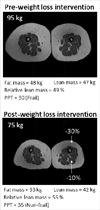

References
-
- Roubenoff R. Sarcopenic obesity: the confluence of two epidemics. Obes Res. 2004;12:887–888. - PubMed
-
- Villareal DT, Banks M, Siener C, Sinacore DR, Klein S. Physical Frailty and Body Composition in Obese Elderly Men and Women. Obes Res. 2004;12:913–920. - PubMed
-
- Kim YS, Lee Y, Chung YS, Lee DJ, Joo NS, Hong D, Song G, Kim HJ, Choi YJ, Kim KM. Prevalence of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity in the Korean population based on the Fourth Korean National Health and Nutritional Examination Surveys. J.Gerontol.A Biol.Sci.Med.Sci. 2012;67:1107–1113. - PubMed
-
- Zizza CA, Herring A, Stevens J, Popkin BM. Obesity affects nursing-care facility admission among whites but not blacks. Obes.Res. 2002;10:816–823. - PubMed
-
- Rantanen T, Harris T, Leveille SG, Visser M, Foley D, Masaki K, Guralnik JM. Muscle strength and body mass index as long-term predictors of mortality in initially healthy men. J.Gerontol.A Biol.Sci.Med.Sci. 2000;55:M168–M173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

