Genome-wide association analysis identifies 13 new risk loci for schizophrenia
- PMID: 23974872
- PMCID: PMC3827979
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.2742
Genome-wide association analysis identifies 13 new risk loci for schizophrenia
Abstract
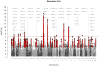
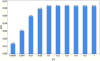
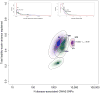
Schizophrenia is an idiopathic mental disorder with a heritable component and a substantial public health impact. We conducted a multi-stage genome-wide association study (GWAS) for schizophrenia beginning with a Swedish national sample (5,001 cases and 6,243 controls) followed by meta-analysis with previous schizophrenia GWAS (8,832 cases and 12,067 controls) and finally by replication of SNPs in 168 genomic regions in independent samples (7,413 cases, 19,762 controls and 581 parent-offspring trios). We identified 22 loci associated at genome-wide significance; 13 of these are new, and 1 was previously implicated in bipolar disorder. Examination of candidate genes at these loci suggests the involvement of neuronal calcium signaling. We estimate that 8,300 independent, mostly common SNPs (95% credible interval of 6,300-10,200 SNPs) contribute to risk for schizophrenia and that these collectively account for at least 32% of the variance in liability. Common genetic variation has an important role in the etiology of schizophrenia, and larger studies will allow more detailed understanding of this disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Saha S, Chant D, McGrath J. A systematic review of mortality in schizophrenia: is the differential mortality gap worsening over time? Archives of general psychiatry. 2007;64:1123–31. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. The Global Burden of Disease: 2004 Update. WHO Press; Geneva: 2008.
-
- Knapp M, Mangalore R, Simon J. The global costs of schizophrenia. Schizophrenia bulletin. 2004;30:279–93. - PubMed
-
- Lichtenstein P, et al. Recurrence risks for schizophrenia in a Swedish national cohort. Psychological Medicine. 2006;36:1417–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 MH095034/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G0400126/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 095552/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 MH077139/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 085475/B/08/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G1100583/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0600429/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0901310/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH083094/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH094421/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- PDA/02/06/016/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- 085475/Z/08/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0601635/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 4584/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- K01 MH094406/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0701420/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0800509/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G1000718/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

