The role of macrophages and dendritic cells in the initiation of inflammation in IBD
- PMID: 23974993
- PMCID: PMC4098861
- DOI: 10.1097/MIB.0b013e3182a69dca
The role of macrophages and dendritic cells in the initiation of inflammation in IBD
Abstract
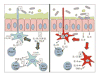
In the healthy gastrointestinal tract, homeostasis is an active process that requires a careful balance of host responses to the enteric luminal contents. Intestinal macrophages and dendritic cells (DCs) comprise a unique group of tissue immune cells that are ideally situated at the interface of the host and the enteric luminal environment to appropriately respond to microbes and ingested stimuli. However, intrinsic defects in macrophage and DC function contribute to the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases, as highlighted by recent genome-wide association studies. Gastrointestinal macrophages and DCs participate in inflammatory bowel disease development through inappropriate responses to enteric microbial stimuli, inefficient clearance of microbes from host tissues, and impaired transition from appropriate proinflammatory responses to anti-inflammatory responses that promote resolution. By understanding how intestinal macrophages and DCs initiate chronic inflammation, new pathogenesis-based therapeutic strategies to treat human inflammatory bowel diseases will be elucidated.
Figures
References
-
- Akira S, Takeda K, Kaisho T. Toll-like receptors: critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:675–680. - PubMed
-
- Janeway CA, Jr, Medzhitov R. Innate immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:197–216. - PubMed
-
- Kawai T, Akira S. Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity. Immunity. 2011;34:637–650. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Danese S. Nonimmune cells in inflammatory bowel disease: from victim to villain. Trends Immunol. 2008;29:555–564. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

