Dynamic MRI of the TMJ under physical load
- PMID: 23975114
- PMCID: PMC3828022
- DOI: 10.1259/dmfr.20120436
Dynamic MRI of the TMJ under physical load
Abstract
Objectives: The objective of this study was to examine the kinematics of structures of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) under physiological load while masticating.
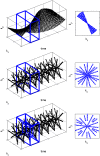
Methods: Radial MRI was chosen as a fast imaging method to dynamically capture the motions of the joint's anatomy. The technique included a golden ratio-based increment angle and a sliding window reconstruction. The measurements were performed on 22 subjects with and without deformation/displacement of the intra-articular disc while they were biting on a cooled caramel toffee.
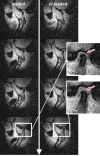
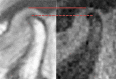
Results: The reconstructed dynamic images provided sufficient information about the size and localization of the disc as well as the change of the intra-articular distance with and without loading.
Conclusions: The feasibility of the golden ratio-based radial MRI technique to dynamically capture the anatomy of the TMJ under physical load was demonstrated in this initial study.
Keywords: magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); temporomandibular joint (TMJ); temporomandibular joint disc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Morphological and positional assessments of TMJ components and lateral pterygoid muscle in relation to symptoms and occlusion of patients with temporomandibular disorders.J Oral Rehabil. 2000 Oct;27(10):860-74. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2842.2000.00622.x. J Oral Rehabil. 2000. PMID: 11065021
-
Biometric parameters of the temporomandibular joint and association with disc displacement and pain: a magnetic resonance imaging study.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013 Jun;42(6):765-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2013.01.004. Epub 2013 Mar 9. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013. PMID: 23490476
-
MRI of the TMJ: morphometric comparison of asymptomatic volunteers and symptomatic patients.Quintessence Int. 2011 Sep;42(8):659-67. Quintessence Int. 2011. PMID: 21842006
-
Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of temporomandibular joint pain during opening and biting in patients with disc displacement.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006 Nov;102(5):669-72. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2005.11.035. Epub 2006 Jun 8. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006. PMID: 17052645
-
Arthroscopic anatomy of the anteromedial wall of the temporomandibular joint: Implications in articular disc displacement.Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2025 Jan;63(1):25-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2024.09.006. Epub 2024 Oct 2. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2025. PMID: 39581790 Review.
Cited by
-
MRI vs. CT for orthodontic applications: comparison of two MRI protocols and three CT (multislice, cone-beam, industrial) technologies.J Orofac Orthop. 2016 Jul;77(4):251-61. doi: 10.1007/s00056-016-0028-2. Epub 2016 Apr 20. J Orofac Orthop. 2016. PMID: 27098643 English.
-
Morphologic Analysis of the Temporomandibular Joint Between Patients With Facial Asymmetry and Asymptomatic Subjects by 2D and 3D Evaluation: A Preliminary Study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Mar;95(13):e3052. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003052. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27043669 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Imaging of the Eye, Optic Nerve, and Extraocular Muscles With Golden Angle Radial MRI.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017 Aug 1;58(10):4390–4398. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-21861. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017. PMID: 28813574 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Utility of Continuous Radial Magnetic Resonance Imaging Acquisition at 3 T in Real-time Patellofemoral Kinematic Assessment: A Feasibility Study.Arthroscopy. 2018 Mar;34(3):726-733. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2017.09.020. Epub 2017 Dec 19. Arthroscopy. 2018. PMID: 29273250 Free PMC article.
-
A simple graded bite block for dynamic magnetic resonance imaging of the temporomandibular joint.Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2022 Jan 1;51(1):20210119. doi: 10.1259/dmfr.20210119. Epub 2021 Jul 8. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34233511 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Okeson JP, Bell WE. Bell’s orofacial pains. Chicago, IL: Quintessence Publishing; 1995
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

