Factors affecting the stability and performance of ipratropium bromide; fenoterol hydrobromide pressurized-metered dose inhalers
- PMID: 23975571
- PMCID: PMC3840779
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-013-0024-4
Factors affecting the stability and performance of ipratropium bromide; fenoterol hydrobromide pressurized-metered dose inhalers
Abstract
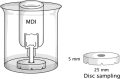
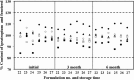
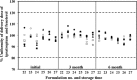
The aim of the study was to investigate the factors affecting the stability and performance of ipratropium bromide and fenoterol hydrobromide in a pressurized-metered dose inhaler (pMDI). A factorial design was applied to investigate the effects of three parameters (propellant, water, and ethanol) on the performance of 27 designed formulations of a solution-based pMDI. The formulations that contained a hydrofluoroalkane (HFA) propellant lower than 72% v/v and an ethanol concentration higher than 27% v/v remained as clear solutions. Nine formulations that contained the HFA propellant higher than 74% v/v precipitated. The results indicated that it was not only the HFA propellant content of the formulations that was related to the formulation instability but also ethanol content. Only six formulations from the 18 formulations, that did not precipitate, produced drug contents that were within the acceptable range (80-120%). These six formulations generated aerosols with mass median aerodynamic diameters (MMAD) of approximately 2 μm with a fine particle fraction (FPF; particle size, <6.4 μm) between 45% and 52%. The MMAD and FPF did not change significantly after 6 months of storage (P > 0.05).
Figures
References
-
- Shrikhande SS, Rao A, Ambekar A, Bajaj AN. Metered dose inhalation formulations for salbutamol sulphate using non-CFC propellant tetrafluoroethane. Int J Pharmaceut Drug Res. 2011;3(4):292–296.
-
- Ibiapina CC, Cruz ÁA, Camargos PAM. Hydrofluoroalkane as a propellant for pressurized metered-dose inhalers: history, pulmonary deposition, pharmacokinetics, efficacy and safety. J Pediatr. 2004;80:441–446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

