Therapeutic PD-1 pathway blockade augments with other modalities of immunotherapy T-cell function to prevent immune decline in ovarian cancer
- PMID: 23975756
- PMCID: PMC3851914
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1550
Therapeutic PD-1 pathway blockade augments with other modalities of immunotherapy T-cell function to prevent immune decline in ovarian cancer
Abstract
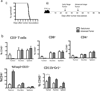
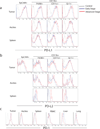
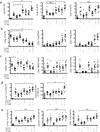
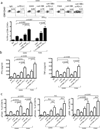
The tumor microenvironment mediates induction of the immunosuppressive programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) pathway, and targeted interventions against this pathway can help restore antitumor immunity. To gain insight into these responses, we studied the interaction between PD-1 expressed on T cells and its ligands (PD-1:PD-L1, PD-1:PD-L2, and PD-L1:B7.1), expressed on other cells in the tumor microenvironment, using a syngeneic orthotopic mouse model of epithelial ovarian cancer (ID8). Exhaustion of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) correlated with expression of PD-1 ligands by tumor cells and tumor-derived myeloid cells, including tumor-associated macrophages (TAM), dendritic cells, and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC). When combined with GVAX or FVAX vaccination (consisting of irradiated ID8 cells expressing granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor or FLT3 ligand) and costimulation by agonistic α-4-1BB or TLR 9 ligand, antibody-mediated blockade of PD-1 or PD-L1 triggered rejection of ID8 tumors in 75% of tumor-bearing mice. This therapeutic effect was associated with increased proliferation and function of tumor antigen-specific effector CD8(+) T cells, inhibition of suppressive regulatory T cells (Treg) and MDSC, upregulation of effector T-cell signaling molecules, and generation of T memory precursor cells. Overall, PD-1/PD-L1 blockade enhanced the amplitude of tumor immunity by reprogramming suppressive and stimulatory signals that yielded more powerful cancer control.
Figures



References
-
- Bukowski RM, Ozols RF, Markman M. The management of recurrent ovarian cancer. Semin Oncol. 2007;34:S1–S15. - PubMed
-
- Ozols RF. Challenges for chemotherapy in ovarian cancer. Ann Oncol. 2006;17(Suppl 5):v181–v187. - PubMed
-
- Chu CS, Kim SH, June CH, Coukos G. Immunotherapy opportunities in ovarian cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2008;8:243–257. - PubMed
-
- Zhang L, Conejo-Garcia JR, Katsaros D, Gimotty PA, Massobrio M, Regnani G, Makrigiannakis A, Gray H, Schlienger K, Liebman MN, Rubin SC, Coukos G. Intratumoral T cells, recurrence, and survival in epithelial ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:203–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

