TBCK influences cell proliferation, cell size and mTOR signaling pathway
- PMID: 23977024
- PMCID: PMC3747267
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071349
TBCK influences cell proliferation, cell size and mTOR signaling pathway
Abstract
Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a central regulator for both cell proliferation and cell growth; however, little is known about the regulation of mTOR expression at the transcriptional level. Here, we provide evidences that a conserved human protein TBCK (TBC1 domain containing kinase) is involved in the regulation of mTOR signaling pathway. Depletion of TBCK significantly inhibits cell proliferation, reduces cell size, and disrupts the organization of actin, but not microtubule. Knockdown of TBCK induces a significant decrease in the protein levels of components of mTOR complex (mTORC), and suppresses the activity of mTOR signaling, but not MAPK or PDK1/Akt pathway. Further results show that TBCK influences the expression of mTORC components at the transcriptional level. Thus, these data suggest that TBCK may play an important role in cell proliferation, cell growth and actin organization possibly by modulating mTOR pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
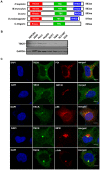



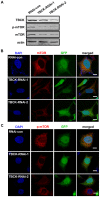



References
-
- Schmelzle T, Hall MN (2000) TOR, a central controller of cell growth. Cell 103: 253–262. - PubMed
-
- Wullschleger S, Loewith R, Hall MN (2006) TOR signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell 124: 471–484. - PubMed
-
- Hay N, Sonenberg N (2004) Upstream and downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev 18: 1926–1945. - PubMed
-
- Kim J, Guan KL (2011) Amino acid signaling in TOR activation. Annu Rev Biochem 80: 1001–1032. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

