Accurate detection and quantification of the fish viral hemorrhagic Septicemia virus (VHSv) with a two-color fluorometric real-time PCR assay
- PMID: 23977162
- PMCID: PMC3748128
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071851
Accurate detection and quantification of the fish viral hemorrhagic Septicemia virus (VHSv) with a two-color fluorometric real-time PCR assay
Abstract
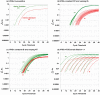
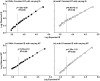
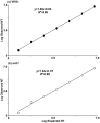
Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia virus (VHSv) is one of the world's most serious fish pathogens, infecting >80 marine, freshwater, and estuarine fish species from Eurasia and North America. A novel and especially virulent strain - IVb - appeared in the Great Lakes in 2003, has killed many game fish species in a series of outbreaks in subsequent years, and shut down interstate transport of baitfish. Cell culture is the diagnostic method approved by the USDA-APHIS, which takes a month or longer, lacks sensitivity, and does not quantify the amount of virus. We thus present a novel, easy, rapid, and highly sensitive real-time quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) assay that incorporates synthetic competitive template internal standards for quality control to circumvent false negative results. Results demonstrate high signal-to-analyte response (slope = 1.00±0.02) and a linear dynamic range that spans seven orders of magnitude (R(2) = 0.99), ranging from 6 to 6,000,000 molecules. Infected fishes are found to harbor levels of virus that range to 1,200,000 VHSv molecules/10(6) actb1 molecules with 1,000 being a rough cut-off for clinical signs of disease. This new assay is rapid, inexpensive, and has significantly greater accuracy than other published qRT-PCR tests and traditional cell culture diagnostics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Rao JR, Fleming CC, Moore JE (2006) Molecular Diagnostics Current Technology and Applications. Horizon Bioscience, Norfolk, Norwich, United Kingdom.
-
- Coutlée F, Viscidi RP, Saint-Antoine P, Kessous A, Yolken RH (1991) The polymerase chain reaction: a new tool for the understanding and diagnosis of HIV-1 infection at the molecular level. Mol Cell Probe 5: 241–259. - PubMed
-
- Ellis JS, Zambon MC (2002) Molecular diagnosis of influenza. Rev Med Virol 12: 375–389. - PubMed
-
- Chai Z, Ma W, Fu F, Lang Y, Wang W, et al. (2013) A SYBR Green-based real-time RT-PCR assay for simple and rapid detection and differentiation of highly pathogenic and classical type 2 porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus circulating in China. Arch Virol 158: 407–415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

