Directed in vitro myogenesis of human embryonic stem cells and their in vivo engraftment
- PMID: 23977197
- PMCID: PMC3747108
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072023
Directed in vitro myogenesis of human embryonic stem cells and their in vivo engraftment
Erratum in
-
Correction: Directed In Vitro Myogenesis of Human Embryonic Stem Cells and Their In Vivo Engraftment.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 18;8(9):10.1371/annotation/b02313dc-840f-4f03-91a2-77cb55a3a4c9. doi: 10.1371/annotation/b02313dc-840f-4f03-91a2-77cb55a3a4c9. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24116259 Free PMC article.
Abstract
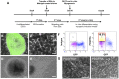
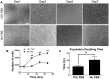
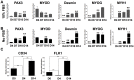
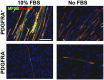
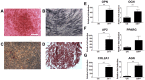
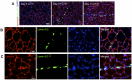
Development of human embryonic stem cell (hESC)-based therapy requires derivation of in vitro expandable cell populations that can readily differentiate to specified cell types and engraft upon transplantation. Here, we report that hESCs can differentiate into skeletal muscle cells without genetic manipulation. This is achieved through the isolation of cells expressing a mesodermal marker, platelet-derived growth factor receptor-α (PDGFRA), following embryoid body (EB) formation. The ESC-derived cells differentiated into myoblasts in vitro as evident by upregulation of various myogenic genes, irrespective of the presence of serum in the medium. This result is further corroborated by the presence of sarcomeric myosin and desmin, markers for terminally differentiated cells. When transplanted in vivo, these pre-myogenically committed cells were viable in tibialis anterior muscles 14 days post-implantation. These hESC-derived cells, which readily undergo myogenic differentiation in culture medium containing serum, could be a viable cell source for skeletal muscle repair and tissue engineering to ameliorate various muscle wasting diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, Waknitz MA, Swiergiel JJ, et al. (1998) Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 282: 1145–1147. - PubMed
-
- Crook JM, Peura TT, Kravets L, Bosman AG, Buzzard JJ, et al. (2007) The Generation of Six Clinical-Grade Human Embryonic Stem Cell Lines. Cell Stem Cell 1: 490–494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

