Impact of a manualized multifocal perinatal home-visiting program using psychologists on postnatal depression: the CAPEDP randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 23977257
- PMCID: PMC3747116
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072216
Impact of a manualized multifocal perinatal home-visiting program using psychologists on postnatal depression: the CAPEDP randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Context: Postnatal maternal depression (PND) is a significant risk factor for infant mental health. Although often targeted alongside other factors in perinatal home-visiting programs with vulnerable families, little impact on PND has been observed.
Objective: This study evaluates the impact on PND symptomatology of a multifocal perinatal home-visiting intervention using psychologists in a sample of women presenting risk factors associated with infant mental health difficulties.
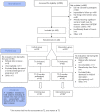
Methods: 440 primiparous women were recruited at their seventh month of pregnancy. All were future first-time mothers, under 26, with at least one of three additional psychosocial risk factors: low educational level, low income, or planning to raise the child without the father. The intervention consisted of intensive multifocal home visits through to the child's second birthday. The control group received care as usual. PND symptomatology was assessed at baseline and three months after birth using the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS).
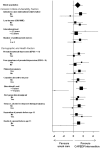
Results: At three months postpartum, mean (SD) EPDS scores were 9.4 (5.4) for the control group and 8.6 (5.4) for the intervention group (p = 0.18). The difference between the mean EPDS scores was 0.85 (95% CI: 0.35; 1.34). The intervention group had significantly lower EPDS scores than controls in certain subgroups: women with few depressive symptoms at inclusion (EPDS <8): difference = 1.66 (95%CI: 0.17; 3.15), p = 0.05, adjusted for baseline EPDS score), women who were planning to raise the child with the child's father: difference = 1.45 (95%CI: 0.27; 2.62), p = 0.04 (adjusted); women with a higher educational level: difference = 1.59 (95%CI: 0.50; 2.68) p = 0.05 (adjusted).
Conclusion: CAPEDP failed to demonstrate an overall impact on PND. However, post-hoc analysis reveals the intervention was effective in terms of primary prevention and in subgroups of women without certain risk factors. Effective overall reduction of PND symptomatology for young, first-time mothers presenting additional psychosocial risk factors may require more tailored interventions.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00392847 Promoting Parental Skills and Enhancing Attachment in Early Childhood (CAPEDP).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Martins C, Gaffan EA (2000) Effects of early maternal depression on patterns of infant-mother attachment: a meta-analytic investigation. Journal of Child Psychology & Psychiatry 41: 737–746. - PubMed
-
- Goodman SH, Brand S (2008) Psychopathology in parents: Clinical issues for children and adolescents. In: Hersen M, Gross AM, editor. Handbook of Clinical Psychology: John Wiley and Sons.
-
- Pawlby S, Sharp D, Hay D, O'Keane V (2008) Postnatal depression and child outcome at 11 years: the importance of accurate diagnosis. Journal of affective disorders 107: 241–245. - PubMed
-
- Murray L, Halligan SL, Adams G, Patterson P, Goodyer IM (2006) Socioemotional development in adolescents at risk for depression: the role of maternal depression and attachment style. Development and Psychopathology 18: 489–516. - PubMed
-
- Gavin NI, Gaynes BN, Lohr KN, Meltzer-Brody S, Gartlehner G, et al. (2005) Perinatal depression: a systematic review of prevalence and incidence. Obstetrics & Gynecology 106: 1071–1083. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

