Human glioblastoma multiforme: p53 reactivation by a novel MDM2 inhibitor
- PMID: 23977270
- PMCID: PMC3747081
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072281
Human glioblastoma multiforme: p53 reactivation by a novel MDM2 inhibitor
Abstract
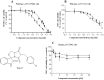
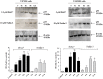
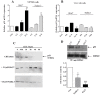
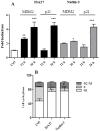
Cancer development and chemo-resistance are often due to impaired functioning of the p53 tumor suppressor through genetic mutation or sequestration by other proteins. In glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), p53 availability is frequently reduced because it binds to the Murine Double Minute-2 (MDM2) oncoprotein, which accumulates at high concentrations in tumor cells. The use of MDM2 inhibitors that interfere with the binding of p53 and MDM2 has become a valid approach to inhibit cell growth in a number of cancers; however little is known about the efficacy of these inhibitors in GBM. We report that a new small-molecule inhibitor of MDM2 with a spirooxoindolepyrrolidine core structure, named ISA27, effectively reactivated p53 function and inhibited human GBM cell growth in vitro by inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. In immunoincompetent BALB/c nude mice bearing a human GBM xenograft, the administration of ISA27 in vivo activated p53, inhibited cell proliferation and induced apoptosis in tumor tissue. Significantly, ISA27 was non-toxic in an in vitro normal human cell model and an in vivo mouse model. ISA27 administration in combination with temozolomide (TMZ) produced a synergistic inhibitory effect on GBM cell viability in vitro, suggesting the possibility of lowering the dose of TMZ used in the treatment of GBM. In conclusion, our data show that ISA27 releases the powerful antitumor capacities of p53 in GBM cells. The use of this MDM2 inhibitor could become a novel therapy for the treatment of GBM patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
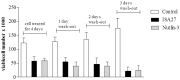
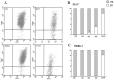
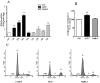
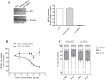
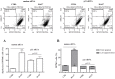
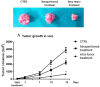
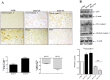
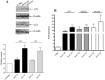
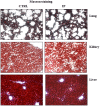
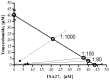
References
-
- Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A, Stommel JM, et al. (2007) Malignant astrocytic glioma: genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. Genes Dev 21: 2683–2710. - PubMed
-
- Ohgaki H, Dessen P, Jourde B, Horstmann S, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004) Genetic pathways to glioblastoma: a population-based study. Cancer Res 64: 6892–6899. - PubMed
-
- Conrad CA, Milosavljevic VP, Yung WK (1995) Advances in chemotherapy for brain tumors. Neurol Clin 13: 795–812. - PubMed
-
- Levin VA, Leibel SA, Gutin PH (2001) Neoplasms of the central nervous system. In: De Vita Jr VT, Hellman S, Rosenberg SA, editors. Cancer principles of oncology. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven. 2100–2161.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

