A meta-analysis of deep hypothermic circulatory arrest versus moderate hypothermic circulatory arrest with selective antegrade cerebral perfusion
- PMID: 23977575
- PMCID: PMC3741839
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2225-319X.2013.03.13
A meta-analysis of deep hypothermic circulatory arrest versus moderate hypothermic circulatory arrest with selective antegrade cerebral perfusion
Abstract
Introduction: A recent concern of deep hypothermic circulatory arrest (DHCA) in aortic arch surgery has been its potential association with increased risk of coagulopathy, elevated inflammatory response and end-organ dysfunction. Recently, moderate hypothermic circulatory arrest (MHCA) with selective antegrade circulatory arrest (SACP) seeks to negate potential hypothermia-related morbidities, while maintaining adequate neuroprotection. The present meta-analysis aims to compare postoperative outcomes in arch surgery using DHCA or MHCA+SACP as neuroprotective strategies.
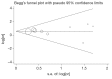
Methods: Electronic searches were performed using six databases from their inception to January 2013. Two reviewers independently identified all relevant studies comparing DHCA with MHCA+SACP, as defined by a recent hypothermia temperature consensus. Data were extracted and meta-analyzed according to pre-defined clinical endpoints.
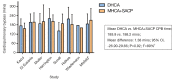
Results: Nine comparative studies were identified for inclusion in the present meta-analysis. Stroke rates were significantly lower in patients undergoing MHCA+SACP (P=0.0007, I(2)=0%), while comparable results were observed with temporary neurological deficit, mortality, renal failure or bleeding. Infrequent and inconsistent reporting of systemic outcomes precluded analysis of other systemic outcomes.
Conclusions: The present meta-analysis indicated the superiority of MHCA+SACP in terms of stroke risk.
Keywords: Deep hypothermic circulatory arrest; antegrade cerebral perfusion; meta-analysis; moderate hypothermic circulatory arrest.
Figures



References
-
- Griepp RB, Stinson EB, Hollingsworth JF, et al. Prosthetic replacement of the aortic arch. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1975;70:1051-63 - PubMed
-
- Stecker MM, Cheung AT, Pochettino A, et al. Deep hypothermic circulatory arrest: I. Effects of cooling on electroencephalogram and evoked potentials. Ann Thorac Surg 2001;71:14-21 - PubMed
-
- McCullough JN, Zhang N, Reich DL, et al. Cerebral metabolic suppression during hypothermic circulatory arrest in humans. Ann Thorac Surg 1999;67:1895-9 - PubMed
-
- Livesay JJ, Cooley DA, Reul GJ, et al. Resection of aortic arch aneurysms: a comparison of hypothermic techniques in 60 patients. Ann Thorac Surg 1983;36:19-28 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
