Pneumosinus dilatans multiplex associated with hormonal imbalance
- PMID: 23978497
- PMCID: PMC3762354
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2013-010345
Pneumosinus dilatans multiplex associated with hormonal imbalance
Abstract
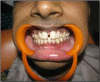
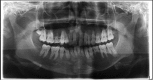
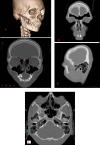
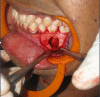
Pneumosinus dilatans describes an abnormal dilation of one or more paranasal sinuses without radiological evidence of localised bone destruction, hyperostosis or mucous membrane thickening. Dilation of mastoid air cells also occurs rarely along with involvement of paranasal sinuses. This rare combination of unknown aetiology was reported in two cases in the literature and termed 'Pneumosinus Dilatans Multiplex' (PSDM). It is usually asymptomatic, and is detected incidentally on plain radiography, CT or MRI. If left untreated, it can further erode the bone leading to complications such as facial asymmetry, neurological disorders and pathological fractures. The aetiology of the condition remains obscure. Various hypotheses proposed are the presence of gas-forming microorganisms, spontaneous drainage of a mucocele, the presence of a one-way valve, dysregulation of hormonal levels leading to a disturbance of osteoblastic and osteoclastic activity. This paper describes a case of PSDM possibly secondary to hormonal disturbance.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pneumosinus dilatans and multiplex: report of three rare cases and review of the literature.Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2007 Jul;36(5):298-303. doi: 10.1259/dmfr/59290441. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2007. PMID: 17586858 Review.
-
Pneumosinus dilatans multiplex, mental retardation, and facial deformity.J Craniofac Surg. 2000 Sep;11(5):487-90. doi: 10.1097/00001665-200011050-00008. J Craniofac Surg. 2000. PMID: 11314069
-
Arachnoid cysts and pneumosinus dilatans.Comput Med Imaging Graph. 1997 Mar-Apr;21(2):125-9. doi: 10.1016/s0895-6111(96)00065-1. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 1997. PMID: 9152578
-
A rare case of pneumosinus dilatans of the frontal sinus and review of the literature.Ann Plast Surg. 1999 Dec;43(6):653-6. doi: 10.1097/00000637-199912000-00014. Ann Plast Surg. 1999. PMID: 10597829 Review.
-
Pneumosinus dilatans: a discussion of four cases and the possible aetiology.Rhinology. 1998 Mar;36(1):40-2. Rhinology. 1998. PMID: 9569442
Cited by
-
Pneumosinus Dilatans frontalis: a case of incidental autopsy diagnosis.Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2019 Dec;15(4):646-648. doi: 10.1007/s12024-019-00120-7. Epub 2019 Jun 3. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31161429
-
Pneumosinus dilatans of the spheno-ethmoidal complex associated with hypovitaminosis D causing bilateral optic canal stenosis.Childs Nerv Syst. 2017 Jun;33(6):1005-1008. doi: 10.1007/s00381-017-3373-6. Epub 2017 Mar 13. Childs Nerv Syst. 2017. PMID: 28289839
-
A Natural History of Silent Brain Syndrome over 36 Years: A case report.Orbit. 2021 Oct;40(5):435-443. doi: 10.1080/01676830.2020.1866023. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Orbit. 2021. PMID: 33722160 Free PMC article.
-
Maxillary Pneumosinus Dilatans Presenting With Proptosis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Clin Med Insights Ear Nose Throat. 2019 Feb 3;12:1179550618825149. doi: 10.1177/1179550618825149. eCollection 2019. Clin Med Insights Ear Nose Throat. 2019. PMID: 30774495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bilateral Visual Loss Caused by Pneumosinus Dilatans: Idiopathic Cases are not Always Reversible.J Curr Ophthalmol. 2021 Jul 5;33(2):197-200. doi: 10.4103/2452-2325.288940. eCollection 2021 Apr-Jun. J Curr Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34409232 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hwang K, Lee DK, Lee CJ, et al. Pneumosinus dilatans multiplex, mental retardation and facial deformity. J Craniofac Surg 2000;2013:487–90 - PubMed
-
- Kiroglu Y, Karabulut N, Sabir NA, et al. Pneumosinus dilatans and multiplex: report of three rare cases and review of the literature. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 2007;2013:298–303 - PubMed
-
- Gardel J, Maduro M. An observation of pneumosinus dilatans [in French]. Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac 1965;2013:619–21 - PubMed
-
- Smith I, Maran A, Von Haacke N. Pneumosinus dilatans. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1987;2013:210–12 - PubMed
-
- Miller NR, Golnik KC, Zeidman SM, et al. Pneumosinus dilatans: a sign of intracranial meningioma. Surg Neurol 1996;2013:471–4 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
