Molecular diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis by gene expression profiling
- PMID: 23978633
- PMCID: PMC4070519
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.08.046
Molecular diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis by gene expression profiling
Abstract
Background & aims: Gene expression profiling provides an opportunity for definitive diagnosis but has not yet been well applied to inflammatory diseases. Here we describe an approach for diagnosis of an emerging form of esophagitis, eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), which is currently diagnosed by histology and clinical symptoms.
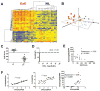
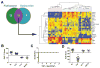
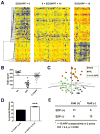
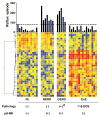
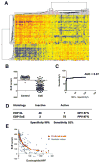
Methods: We developed an EoE diagnostic panel (EDP) comprising a 96-gene quantitative polymerase chain reaction array and an associated dual-algorithm that uses cluster analysis and dimensionality reduction using a cohort of randomly selected esophageal biopsy samples from pediatric patients with EoE (n = 15) or without EoE (non-EoE controls, n = 14) and subsequently vetted the EDP using a separate cohort of 194 pediatric and adult patient samples derived from both fresh or formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue: active EoE (n = 91), control (non-EoE and EoE remission, n = 57), histologically ambiguous (n = 34), and reflux (n = 12) samples.
Results: The EDP identified adult and pediatric patients with EoE with approximately 96% sensitivity and approximately 98% specificity, and distinguished patients with EoE in remission from controls, as well as identified patients exposed to swallowed glucorticoids. The EDP could be used with formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue RNA and distinguished patients with EoE from those with reflux esophagitis, identified by pH-impedance testing. Preliminary evidence showed that the EDP could identify patients likely to have disease relapse after treatment.
Conclusions: We developed a molecular diagnostic test (referred to as the EDP) that identifies patients with esophagitis in a fast, objective, and mechanistic manner, offering an opportunity to improve diagnosis and treatment, and a platform approach for other inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: AUC; Diagnostic Panel; EDP; EGID; EoE; EoE Transcriptome; Eosinophil; FFPE; Fluidic Card; GERD; GI; HPF; MII; NL; Nonerosive Reflux Disease; ROC; Signature; area under the curve; eosinophilic esophagitis; eosinophilic esophagitis diagnostic panel; eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorder; formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded; gastroesophageal reflux disease; gastrointestinal; high-power field; multichannel intraluminal impedance; normal; receiver operating characteristic.
Copyright © 2013 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Liacouras CA, Furuta GT, Hirano I, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: updated consensus recommendations for children and adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128:3–20. e6. quiz 21–2. - PubMed
-
- Hruz P, Straumann A, Bussmann C, et al. Escalating incidence of eosinophilic esophagitis: a 20-year prospective, population-based study in Olten County, Switzerland. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128:1349–1350. e5. - PubMed
-
- Veerappan GR, Perry JL, Duncan TJ, et al. Prevalence of eosinophilic esophagitis in an adult population undergoing upper endoscopy: a prospective study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7:420–6. 426 e1–2. - PubMed
-
- Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Collins MH, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults: a systematic review and consensus recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:1342–63. - PubMed
-
- Remedios M, Campbell C, Jones DM, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults: clinical, endoscopic, histologic findings, and response to treatment with fluticasone propionate. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006;63:3–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

