Hindbrain orexin 1 receptors influence palatable food intake, operant responding for food, and food-conditioned place preference in rats
- PMID: 23978908
- PMCID: PMC3946976
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-013-3248-9
Hindbrain orexin 1 receptors influence palatable food intake, operant responding for food, and food-conditioned place preference in rats
Abstract
Rationale: Brain orexin 1 receptors (OX1Rs) are involved in food-motivated behavior. Most research has focused on forebrain OX1R populations, but hindbrain OX1Rs affect feeding. We hypothesized that hindbrain OX1Rs affect the reward value of food.
Objectives: We examined the effects of hindbrain OX1R stimulation or blockade on motivation for food, palatable high-fat (HF) food intake, and food-conditioned place preference.
Methods: Rats trained to lever press for sucrose on a progressive ratio (PR) schedule received fourth intracerebroventricular (icv) injections of vehicle, orexin-A (0.1-1 nmol), or the OX1R antagonist SB334867 (10-20 nmol) before operant test sessions. Effects of these treatments on HF food intake during daily 1-h tests were assessed with fourth icv and nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) injections. We conditioned a place preference by pairing HF food with one side of a two-sided chamber and then examined the effect of 20 nmol fourth icv SB334867 on the expression of that preference.
Results: In ad lib fed rats on the PR schedule, fourth icv orexin-A significantly increased responding and breakpoint relative to the vehicle. In 24-h food-deprived rats, fourth icv SB334867 significantly decreased responding and breakpoint. Orexin-A delivered to the fourth ventricle (0.1 nmol) or NTS (0.01 nmol) increased HF diet intake. Fourth icv SB334867 did not affect HF food intake, but SB334867 delivered either fourth icv (20 nmol) or intra-NTS (5-10 nmol) suppressed chow intake. Expression of HF food-conditioned place preference was inhibited by fourth icv SB334867.
Conclusions: Hindbrain OX1R activity affects food-motivated operant behavior and may play a role in responding to cues that predict palatable food.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
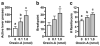
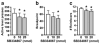
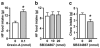


Similar articles
-
Orexin-1 receptor mediates the increased food and water intake induced by intracerebroventricular injection of the stable somatostatin pan-agonist, ODT8-SST in rats.Neurosci Lett. 2014 Jul 25;576:88-92. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2014.05.063. Epub 2014 Jun 7. Neurosci Lett. 2014. PMID: 24915296 Free PMC article.
-
Hindbrain orexin 1 receptors blunt intake suppression by gastrointestinal nutrients and cholecystokinin in male rats.Peptides. 2020 Nov;133:170351. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2020.170351. Epub 2020 Jun 21. Peptides. 2020. PMID: 32579900 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for the role of hindbrain orexin-1 receptors in the control of meal size.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011 Dec;301(6):R1692-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00044.2011. Epub 2011 Sep 28. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21957165 Free PMC article.
-
Orexin signaling via the orexin 1 receptor mediates operant responding for food reinforcement.Biol Psychiatry. 2010 Apr 15;67(8):753-60. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.12.035. Epub 2010 Feb 26. Biol Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 20189166 Free PMC article.
-
Role of orexin/hypocretin in reward-seeking and addiction: implications for obesity.Physiol Behav. 2010 Jul 14;100(5):419-28. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2010.03.009. Epub 2010 Mar 23. Physiol Behav. 2010. PMID: 20338186 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of the GLP-1 receptors in the nucleus of the solitary tract reduces food reward behavior and targets the mesolimbic system.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 20;10(3):e0119034. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119034. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25793511 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin and adiponectin regulate the activity of nuclei involved in sleep-wake cycle in male rats.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jul 22;16:907508. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.907508. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35937866 Free PMC article.
-
Growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF15) and semaglutide inhibit food intake and body weight through largely distinct, additive mechanisms.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2022 Jun;24(6):1010-1020. doi: 10.1111/dom.14663. Epub 2022 Mar 7. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2022. PMID: 35129264 Free PMC article.
-
Orexin-1 receptor mediates the increased food and water intake induced by intracerebroventricular injection of the stable somatostatin pan-agonist, ODT8-SST in rats.Neurosci Lett. 2014 Jul 25;576:88-92. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2014.05.063. Epub 2014 Jun 7. Neurosci Lett. 2014. PMID: 24915296 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of reward signalling and appetite regulating peptide systems in the control of food-cue responses.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Nov;172(22):5225-38. doi: 10.1111/bph.13321. Epub 2015 Nov 1. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26403657 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blevins JE, Stanley BG, Reidelberger RD. DMSO as a vehicle for central injections: tests with feeding elicited by norepinephrine injected into the paraventricular nucleus. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2002;71:277–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

