Pharmacokinetics and safety of tenofovir in HIV-infected women during labor and their infants during the first week of life
- PMID: 23979002
- PMCID: PMC3912736
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e3182a921eb
Pharmacokinetics and safety of tenofovir in HIV-infected women during labor and their infants during the first week of life
Abstract
Background: Data describing the pharmacokinetics and safety of tenofovir in neonates are lacking.
Methods: The HIV Prevention Trials Network 057 protocol was a phase 1, open-label study of the pharmacokinetics and safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) in HIV-infected women during labor and their infants during the first week of life with 4 dosing cohorts: maternal 600 mg doses/no infant dosing; no maternal dosing/infant 4 mg/kg doses on days 0, 3, and 5; maternal 900 mg doses/infant 6 mg/kg doses on days 0, 3, and 5; maternal 600 mg doses/infant 6 mg/kg daily for 7 doses. Pharmacokinetic sampling was performed on cohort 1 and 3 mothers and all infants. Plasma, amniotic fluid, and breast milk tenofovir concentrations were determined by liquid chromatographic-tandem mass spectrometric assay. The pharmacokinetic target was for infant tenofovir concentration throughout the first week of life to exceed 50 ng/mL, the median trough tenofovir concentration in adults receiving standard chronic TDF dosing.
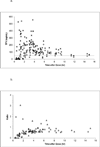
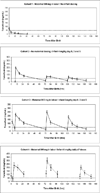
Results: One hundred twenty-two mother-infant pairs from Malawi and Brazil were studied. Tenofovir exposure in mothers receiving 600 and 900 mg exceeded that in nonpregnant adults receiving standard 300 mg doses. Tenofovir elimination in the infants was equivalent to that in older children and adults, and trough tenofovir plasma concentrations exceeded 50 ng/mL in 74%-97% of infants receiving daily dosing.
Conclusions: A TDF dosing regimen of 600 mg during labor and daily infant doses of 6 mg/kg maintains infant tenofovir plasma concentration above 50 ng/mL throughout the first week of life and should be used in the studies of TDF efficacy for HIV prevention of mother-to-child transmission and early infant treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: For the remaining authors no conflicts were declared.
Figures

References
-
- Townsend CL, Cortina-Borja M, Peckham CS, de Ruiter A, Lyall H, Tookey PA. Low rates of mother-to-child transmission of HIV following effective pregnancy interventions in the United Kingdom and Ireland, 2000–2006. AIDS. 2008 May 11;22(8):973–981. - PubMed
-
- Van Rompay KK, Berardi CJ, Aguirre NL, et al. Two doses of PMPA protect newborn macaques against oral simian immunodeficiency virus infection. AIDS. 1998 Jun 18;12(9):F79–F83. - PubMed
-
- Van Rompay KK, Marthas ML, Lifson JD, et al. Administration of 9-[2-(phosphonomethoxy)propyl]adenine (PMPA) for prevention of perinatal simian immunodeficiency virus infection in rhesus macaques. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1998 Jun 10;14(9):761–773. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HHSN267200800001G/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068632/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI046749/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069518/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068616/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN267200800001C/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI041110/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068616/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI068632/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-001/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068632/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1 U01 AI068616/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5 U01 AI41110/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

