Adaptive response in human blood lymphocytes exposed to non-ionizing radiofrequency fields: resistance to ionizing radiation-induced damage
- PMID: 23979077
- PMCID: PMC3951069
- DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rrt106
Adaptive response in human blood lymphocytes exposed to non-ionizing radiofrequency fields: resistance to ionizing radiation-induced damage
Abstract
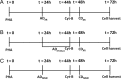
The aim of this preliminary investigation was to assess whether human peripheral blood lymphocytes which have been pre-exposed to non-ionizing radiofrequency fields exhibit an adaptive response (AR) by resisting the induction of genetic damage from subsequent exposure to ionizing radiation. Peripheral blood lymphocytes from four healthy donors were stimulated with phytohemagglutinin for 24 h and then exposed for 20 h to 1950 MHz radiofrequency fields (RF, adaptive dose, AD) at an average specific absorption rate of 0.3 W/kg. At 48 h, the cells were subjected to a challenge dose (CD) of 1.0 or 1.5 Gy X-irradiation (XR, challenge dose, CD). After a 72 h total culture period, cells were collected to examine the incidence of micronuclei (MN). There was a significant decrease in the number of MN in lymphocytes exposed to RF + XR (AD + CD) as compared with those subjected to XR alone (CD). These observations thus suggested a RF-induced AR and induction of resistance to subsequent damage from XR. There was variability between the donors in RF-induced AR. The data reported in our earlier investigations also indicated a similar induction of AR in human blood lymphocytes that had been pre-exposed to RF (AD) and subsequently treated with a chemical mutagen, mitomycin C (CD). Since XR and mitomycin-C induce different kinds of lesions in cellular DNA, further studies are required to understand the mechanism(s) involved in the RF-induced adaptive response.
Keywords: X-rays; adaptive response; human lymphocytes; micronucleus; radiofrequency.
Figures


References
-
- Olivieri G, Bodycote J, Wolff S. Adaptive response of human lymphocytes to low concentrations of radioactive thymidine. Science. 1984;223:594–7. - PubMed
-
- Wiencke J-K, Afzal V, Olivieri G, et al. Evidence that the [3H]thymidine induced adaptive response in human lymphocytes to subsequent doses of X-rays involves the induction of a chromosomal repair mechanism. Mutagenesis. 1986;1:375–80. - PubMed
-
- Shadley J-D, Afzal V, Wolff S. Characterization of the adaptive response to ionizing radiation induced by low doses of X-rays to human lymphocytes. Radiat Res. 1987;111:511–7. - PubMed
-
- Bosi A, Olivieri G. Variability of the adaptive response to ionizing radiation in humans. Mutat Res. 1989;211:13–7. - PubMed
-
- Vijayalaxmi, Burkart W. Resistance and cross-resistance to chromosome damage in human blood lymphocytes exposed to bleomycin. Mutat Res. 1989a;211:1–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

