Characterization of two ENU-induced mutations affecting mouse skeletal morphology
- PMID: 23979929
- PMCID: PMC3789799
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.113.007310
Characterization of two ENU-induced mutations affecting mouse skeletal morphology
Abstract
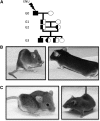
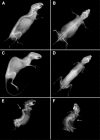
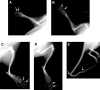
Using the N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU) mutagenesis screen, we have identified two skeletal morphology mutants, Skm1 and Skm2. Positional cloning and candidate gene sequencing localized the causative point mutations within the genes coding for natriuretic peptide receptor C (NPR-C) and filamin b (FLNB), respectively. Mice that carry a mutation in Npr3 exhibit a skeletal overgrowth phenotype, resulting in an elongated body and kyphosis. Skm2 mice, carrying a mutation in Flnb, present with scoliosis and lordosis. These mutant mice will serve as useful models for the study of vertebral malformations.
Figures


References
-
- Hensinger R. N., 2009. Congenital scoliosis: etiology and associations. Spine 34: 1745–1750 - PubMed
-
- Kesling K.L., Reinker K.A. 1997. Scoliosis in twins. A meta-analysis of the literature and report of six cases. Spine 22: 2009–2015. - PubMed
-
- Krakow D., Robertson S. P., King L. M., Morgan T., Sebald E. T., et al. , 2004. Mutations in the gene encoding filamin B disrupt vertebral segmentation, joint formation and skeletogenesis. Nat. Genet. 36: 405–410 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
