Integrative radiogenomic profiling of squamous cell lung cancer
- PMID: 23980093
- PMCID: PMC3856255
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1616
Integrative radiogenomic profiling of squamous cell lung cancer
Abstract
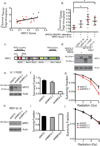
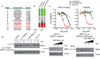
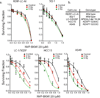
Radiotherapy is one of the mainstays of anticancer treatment, but the relationship between the radiosensitivity of cancer cells and their genomic characteristics is still not well defined. Here, we report the development of a high-throughput platform for measuring radiation survival in vitro and its validation in comparison with conventional clonogenic radiation survival analysis. We combined results from this high-throughput assay with genomic parameters in cell lines from squamous cell lung carcinoma, which is standardly treated by radiotherapy, to identify parameters that predict radiation sensitivity. We showed that activation of NFE2L2, a frequent event in lung squamous cancers, confers radiation resistance. An expression-based, in silico screen nominated inhibitors of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) as NFE2L2 antagonists. We showed that the selective PI3K inhibitor, NVP-BKM120, both decreased NRF2 protein levels and sensitized NFE2L2 or KEAP1-mutant cells to radiation. We then combined results from this high-throughput assay with single-sample gene set enrichment analysis of gene expression data. The resulting analysis identified pathways implicated in cell survival, genotoxic stress, detoxification, and innate and adaptive immunity as key correlates of radiation sensitivity. The integrative and high-throughput methods shown here for large-scale profiling of radiation survival and genomic features of solid-tumor-derived cell lines should facilitate tumor radiogenomics and the discovery of genotype-selective radiation sensitizers and protective agents.
©2013 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: M.M. is a consultant to Novartis and receives research support from Novartis, and is a founding advisor and consultant to, and an equity holder in, Foundation Medicine. P.S.H. reports consulting fees from ARIAD.
Figures

References
-
- Curran WJ. New chemotherapeutic agents: update of major chemoradiation trials in solid tumors. Oncology (Williston Park) 2002;63(Suppl 2):29–38. - PubMed
-
- Hammerman PS, Janne PA, Johnson BE. Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:7502–7509. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–1500. - PubMed
-
- Amundson SA, Do KT, Vinikoor LC, Lee RA, Koch-Paiz CA, Ahn J, et al. Integrating global gene expression and radiation survival parameters across the 60 cell lines of the National Cancer Institute Anticancer Drug Screen. Cancer research. 2008;68:415–424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RC2 CA148399/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM038627/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32CA009382-30/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA122794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA163677/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM038627/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 CA140594/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA121941/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA154303/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA109038/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009382/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA166480/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 CA138399-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GM38627/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA154480/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

