CD38 controls the innate immune response against Listeria monocytogenes
- PMID: 23980105
- PMCID: PMC3811837
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00340-13
CD38 controls the innate immune response against Listeria monocytogenes
Abstract
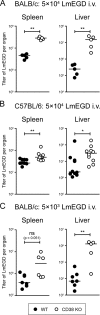
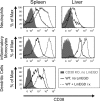
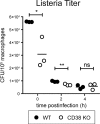
CD38, adenosine-5'-diphosphate-ribosyl cyclase 1, is a multifunctional enzyme, expressed on a wide variety of cell types. CD38 has been assigned diverse functions, including generation of calcium-mobilizing metabolites, cell activation, and chemotaxis. Using a murine Listeria monocytogenes infection model, we found that CD38 knockout (KO) mice were highly susceptible to infection. Enhanced susceptibility was already evident within 3 days of infection, suggesting a function of CD38 in the innate immune response. CD38 was expressed on neutrophils and inflammatory monocytes, and especially inflammatory monocytes further upregulated CD38 during infection. Absence of CD38 caused alterations of the migration pattern of both cell types to sites of infection. We observed impaired accumulation of cells in the spleen but surprisingly similar or even higher accumulation of cells in the liver. CD38 KO and wild-type mice showed similar changes in the composition of neutrophils and inflammatory monocytes in blood and bone marrow, indicating that mobilization of these cells from the bone marrow was CD38 independent. In vitro, macrophages of CD38 KO mice were less efficient in uptake of listeria but still able to kill the bacteria. Dendritic cells also displayed enhanced CD38 expression following infection. However, absence of CD38 did not impair the capacity of mice to prime CD8(+) T cells against L. monocytogenes, and CD38 KO mice could efficiently control secondary listeria infection. In conclusion, our results demonstrate an essential role for CD38 in the innate immune response against L. monocytogenes.
Figures


References
-
- Lund F, Solvason N, Grimaldi JC, Parkhouse RM, Howard M. 1995. Murine CD38: an immunoregulatory ectoenzyme. Immunol. Today 16:469–473 - PubMed
-
- Yamada M, Mizuguchi M, Otsuka N, Ikeda K, Takahashi H. 1997. Ultrastructural localization of CD38 immunoreactivity in rat brain. Brain Res. 756:52–60 - PubMed
-
- Sun L, Adebanjo OA, Koval A, Anandatheerthavarada HK, Iqbal J, Wu XY, Moonga BS, Wu XB, Biswas G, Bevis PJ, Kumegawa M, Epstein S, Huang CL, Avadhani NG, Abe E, Zaidi M. 2002. A novel mechanism for coupling cellular intermediary metabolism to cytosolic Ca2+ signaling via CD38/ADP-ribosyl cyclase, a putative intracellular NAD+ sensor. FASEB J. 16:302–314 - PubMed
-
- Zhao YJ, Lam CM, Lee HC. 2012. The membrane-bound enzyme CD38 exists in two opposing orientations. Sci. Signal. 5:ra67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

