Decarboxylative palladium(II)-catalyzed synthesis of aryl amidines from aryl carboxylic acids: development and mechanistic investigation
- PMID: 23983102
- PMCID: PMC3935511
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.201301809
Decarboxylative palladium(II)-catalyzed synthesis of aryl amidines from aryl carboxylic acids: development and mechanistic investigation
Abstract
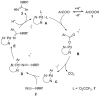
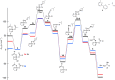
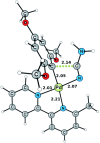
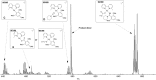
A fast and convenient synthesis of aryl amidines starting from carboxylic acids and cyanamides is reported. The reaction was achieved by palladium(II)-catalysis in a one-step microwave protocol using [Pd(O2 CCF3 )2 ], 6-methyl-2,2'-bipyridyl and trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) in N-methylpyrrolidinone (NMP), providing the corresponding aryl amidines in moderate to excellent yields. The protocol is very robust with regards to the cyanamide coupling partner but requires electron-rich ortho-substituted aryl carboxylic acids. Mechanistic insight was provided by a DFT investigation and direct ESI-MS studies of the reaction. The results of the DFT study correlated well with the experimental findings and, together with the ESI-MS study, support the suggested mechanism. Furthermore, a scale-out (scale-up) was performed with a non-resonant microwave continuous-flow system, achieving a maximum throughput of 11 mmol h(-1) by using a glass reactor with an inner diameter of 3 mm at a flow rate of 1 mL min(-1) .
Keywords: decarboxylation; density functional calculations; mass spectrometry; microwave chemistry; palladium.
© 2013 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA. This is an open access article under the terms of Creative Commons the Attribution Non-Commercial NoDerivs License, which permits use and distribution in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited, the use is non-commercial and no modifications or adaptations are made.
Figures


References
-
- Rodríguez N, Goossen LJ. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011;40:5030–5048. - PubMed
-
- Shepard AF, Winslow NR, Johnson JR. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1930;52:2083–2090.
-
- Voutchkova A, Coplin A, Leadbeater NE, Crabtree RH. Chem. Commun. 2008;47:6312–6314. - PubMed
-
- Dai J-J, Liu J-H, Luo D-F, Liu L. Chem. Commun. 2011;47:677–679. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

