Trichilia monadelpha bark extracts inhibit carrageenan-induced foot-oedema in the 7-day old chick and the oedema associated with adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats
- PMID: 23983314
- PMCID: PMC3744209
- DOI: 10.4314/ajtcam.v9i1.2
Trichilia monadelpha bark extracts inhibit carrageenan-induced foot-oedema in the 7-day old chick and the oedema associated with adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats
Abstract
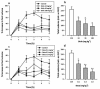
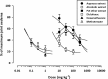
Trichilia monadelpha (Thonn) JJ De Wilde (Meliaceae) bark extract is used in African traditional medicine for the management of various disease conditions including inflammatory disorders such as arthritis. The present study was undertaken to evaluate the anti-inflammatory properties of aqueous (TWE), alcoholic (TAE) and petroleum ether extract (TPEE) of T. monadelpha using the 7-day old chick-carrageenan footpad oedema (acute inflammation) and the adjuvant-induced arthritis model in rats (chronic inflammation). TWE and TPEE significantly inhibited the chick-carrageenan footpad oedema with maximal inhibitions of 57.79±3.92 and 63.83±12 respectively, but TAE did not. The reference anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac and dexamethasone) inhibited the chick-carrageenan-induced footpad oedema, with maximal inhibitions of 64.92±2.03 and 71.85±15.34 respectively. Furthermore, all the extracts and the reference anti-inflammatory agents (diclofenac, dexamethasone, methotrexate) inhibited the inflammatory oedema associated with adjuvant arthritis with maximal inhibitions of 64.41±5.56, 57.04±8.57, 62.18±2.56%, for TWE, TAE and TPEE respectively and 80.28±5.79, 85.75±2.96, 74.68±3.03% for diclofenac, dexamethasone and methotrexate respectively. Phytochemical screening of the plant bark confirmed the presence of a large array of plant constituents such as alkaloids, glycosides, flavonoids, saponins, steroids, tannins and terpenoids, all of which may be potential sources of phyto-antiinflammatory agents. In conclusion, our work suggests that T. monadelpha is a potential source of antiinflammatory agents.
Keywords: Antiinflammatory; Arthritis; Trichilia monadelpha; chick-carrageenan; phyto-antiinflammatory.
Figures




References
-
- Abbiw D K. Useful Plants of Ghana. Kew: Intermediate Tecgnology Publications and The Royal Botanic Gardens; 1990.
-
- Abiodun F, Ching F P A, Sunday A A, Odion E. Phytochemical and Antiinflammatory Evaluation of Khaya grandifoliola Stem Bark Extract. Int J PharmTech Res. 2009;1:1061–1064.
-
- Adebayo E A, Ishola O R. Phytochemical and antimicrobial screening of the crude extracts from the root, stem bark and leaves of Bridelia ferruginea. Afr J Biotechnol. 2009;8:650–653.
-
- Aladesanmi A J, Odediran S A. Antimicrobial activity of Trichilia heudelotti leaves. Fitoterapia. 2000;71:179–182. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
