The immunomodulatory effects of Sutherlandia frutescens extracts in human normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- PMID: 23983354
- PMCID: PMC3746609
- DOI: 10.4314/ajtcam.v9i3s.6
The immunomodulatory effects of Sutherlandia frutescens extracts in human normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells
Abstract
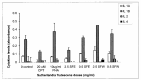
Sutherlandia frutescens (SF) is one of the medicinal plants used as an immune booster in the treatment of chronic ailments such as HIV/AIDS and cancer. Limited data suggest that its efficacy is based on its regulatory effect on cytokines, the critical components of the immune response. In this study, we investigated the in vitro immunomodulatory effects of SF extracts on normal human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). An ELISA-based assay was used to assess the levels of expression of 12 cytokines in treated cells. An adenosine triphosphate (ATP) assay was used to assess cell viability in relation to cytokine secretion. SF ethanol extracts induced changes in cytokine secretion relative to the dose of the extract. Generally cytokine expression and secretion was low in concentration because were not stimulated with any endotoxin. The high SFE dose (2.5 mg/ml) significantly (p<0.001) decreased some cytokines including TNF-α and IL 1β. Low doses of this extract (0.5 mg/ml) did not change TNF-α and IL 1β secretion from the baseline (untreated cells). Changes in cytokine secretion of SFE treated cells tracked changes in ATP levels (cell viability). The SFW extract-induced changes in cytokine secretion were independent of cell viability. TNF-α was decreased (p<0.001) by the high dose of SFW extract while IL 1β and IFNγ were increased (p<0.01) by the same dose. High doses decreased cell viability which was reflected in cytokine secretion. It is evident, from these results, that SF extracts can modulate cytokine secretion in unstimulated normal PBMCs in vitro. Further studies in animal models are recommended to advance understanding of this immunomodulatory activity.
Keywords: ELISA; Sutherlandia frutescens; cell viability; cytokines; immune response.
Figures



References
-
- Alfano M, Poli G. Role of cytokines and chemokines in the regulation of innate immunity and HIV infection. Mol Immunol. 2005;42:161–182. - PubMed
-
- Borish LC, Steinke JW. Cytokines and chemokines. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;111:460–475. - PubMed
-
- Chabalala H. African Traditional Medicines: The Role of Indigenous Knowledge Systems in Bioprospecting and Product Development in South Africa; Paper as presented at the 2008 Rebuild Africa Conference; August 8–9; Washington DC. 2008.
-
- Chinkwo KA. Sutherlandia frutescens extracts can induce apoptosis in cultured carcinoma cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 2005;98:163–170. - PubMed
-
- Fernandes AC, Cromarty AD, Albrecht A, van Rensburg CE. The antioxidant potential of Sutherlandia frutescens. J Ethnopharmacol. 2004;95:1–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
