Hyperammonemic coma in a post-partum patient with undiagnosed urea cycle defect
- PMID: 23983417
- PMCID: PMC3752861
- DOI: 10.4103/0972-5229.114816
Hyperammonemic coma in a post-partum patient with undiagnosed urea cycle defect
Abstract
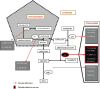
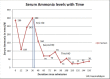
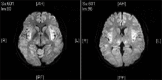
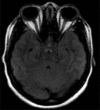
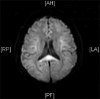
Urea cycle disorders (UCD) are common during neonatal period, and it is rarely reported in adults. We are reporting a patient presenting with post-partum neuropsychiatric symptoms rapidly progressing to coma. Markedly raised serum ammonia level on presentation with an initial normal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of brain and normal liver function tests led to the suspicion of UCD, which was confirmed on the basis of urine orotic acid and elevated serum amino acid levels. We had to resort to hemodialysis to correct the hyperammonemic coma, which was unresponsive to conventional anti-ammonia measures. She exhibited remarkable improvement with a progressive decline in serum ammonia with repeated hemodialysis and made a full recovery. Timely diagnosis and early institution of hemodialysis in the setting of a poor neurological status maybe considered a suitable treatment option.
Keywords: Hyperammonemic coma; post-partum patient; urea cycle defect.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Summar ML, Tuchman M. Urea Cycle Disorders Overview. [Last accessed on 2003 Apr 6]. Available from: http://www.geneclinics.org/servlet/access?id=8888891andkey=GUBxuTEL2m2Zh... .
-
- Batshaw ML. Hypeammonemia. Curr Probl Pediatr. 1984;14:1–69. - PubMed
-
- Kotani Y, Shiota M, Umemoto M, Tsuritani M, Hoshiai H. Carbamyl phosphate synthetase deficiency and postpartum hyperammonemia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2010;203:e10–1. - PubMed
-
- Tuchman M, Holzknecht RA. Heterogeneity of patient with late onset ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. Clin Invest Med. 1991;14:320–4. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
