The possible mechanisms underlying the impairment of HIF-1α pathway signaling in hyperglycemia and the beneficial effects of certain therapies
- PMID: 23983604
- PMCID: PMC3752727
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.5630
The possible mechanisms underlying the impairment of HIF-1α pathway signaling in hyperglycemia and the beneficial effects of certain therapies
Abstract
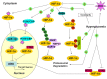
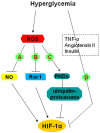
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1α), an essential transcription factor which mediates the adaptation of cells to low oxygen tensions, is regulated precisely by hypoxia and hyperglycemia, which are major determinants of the chronic complications associated with diabetes. The process of HIF-1α stabilization by hypoxia is clear; however, the mechanisms underlying the potential deleterious effect of hyperglycemia on HIF-1α are still controversial, despite reports of a variety of studies demonstrating the existence of this phenomenon. In fact, HIF-1α and glucose can sometimes influence each other: HIF-1α induces the expression of glycolytic enzymes and glucose metabolism affects HIF-1α accumulation in some cells. Although hyperglycemia upregulates HIF-1α signaling in some specific cell types, we emphasize the inhibition of HIF-1α by high glucose in this review. With regard to the mechanisms of HIF-1α impairment, the role of methylglyoxal in impairment of HIF-1α stabilization and transactivation ability and the negative effect of reactive oxygen species (ROS) on HIF-1α are discussed. Other explanations for the inhibition of HIF-1α by high glucose exist: the increased sensitivity of HIF-1α to Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) machinery, the role of osmolarity and proteasome activity, and the participation of several molecules. This review aims to summarize several important developments regarding these mechanisms and to discuss potentially effective therapeutic techniques (antioxidants eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and metallothioneins (MTs), pharmaceuticals cobalt chloride (CoCl2), dimethyloxalylglycine (DMOG), desferrioxamine (DFO) and gene transfer of constitutively active forms of HIF-1α) and their mechanisms of action for intervention in the chronic complications in diabetes.
Keywords: Hyperglycemia; Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1α); Methylglyoxal (MGO); Prolyl hydroxylases (PHDs); Reactive oxidative species (ROS); Therapy..
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Jiang BH, Semenza GL, Bauer C, Marti HH. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 levels vary exponentially over a physiologically relevant range of O2 tension. Am J Physiol. 1996;271:C1172–C1180. - PubMed
-
- Huang LE, Arany Z, Livingston DM, Bunn HF. Activation of hypox-ia-inducible transcription factor depends primarily upon re-dox-sensitive stabilization of its alpha subunit. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:32253–32259. - PubMed
-
- Jaakkola P, Mole DR, Tian YM, Wilson MI, Gielbert J, Gaskell SJ. et al. Targeting of HIF-1α to the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl hydroxylation. Science. 2001;292:468–472. - PubMed
-
- Salnikow K, Donald SP, Bruick RK, Zhitkovich A, Phang JM, Kasprzak KS. Depletion of intracellular ascorbate by the carcinogenic metals nickel and cobalt results in the induction of hypoxic stress. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:40337–40344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

